AWS
AWS's Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service) offers a powerful and flexible way to securely store large amounts of unstructured data—such as images, videos, or documents—in the cloud. Access keys and predefined authorization policies (IAM roles or signed URLs) can be used to precisely control access to stored content and grant individual permissions. This allows data to be uploaded, retrieved, and processed from any location—without direct interaction with the AWS console. Amazon S3 is ideal for applications that require centralized, scalable, and highly available data storage. In addition, the service supports various storage classes, access levels, and integrations, allowing it to fit seamlessly into existing workflows and applications. This guide provides step-by-step instructions on how to configure Amazon S3, upload data, and manage it securely.
Connection Parameter
Parameter | Type | Unit | Explanation | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Payload | Byte Array | The byte array contains the message data to be transferred. It can include various file formats, e.g., images, videos, or other files to be uploaded. | Image from “Image to JPG” node | |
Region | String | Defines the AWS region in which the S3 bucket is created. It affects latency, availability, and legal requirements for data storage. The region cannot be chosen arbitrarily, but is already determined when AWS or S3 storage is set up. | ||
Bucket | String | Refers to the name of the S3 bucket in which files are stored. The name must be globally unique and is used when uploading and retrieving files. | pictures | |
Access Key Id | String | A public identifier for AWS access credentials. It is used together with the secret key to enable authenticated access to the S3 service. |
| |
Secret Access Key | String - Secret | The private part of the AWS access data. It is required for authentication and should never be stored or transmitted publicly. |
| |
Directory | String | Specifies a subfolder in the bucket. If it already exists, data is stored there. Otherwise, it is created automatically. If not specified, data is stored directly in the bucket. | meinUnterordner | |
Filename | String | Defines the name of the file to be transferred. The file name can be generated dynamically and is stored together with the file to enable unique identification. | 20250731_112200_bild1.jpg | |
Timeout | Integer | ms | Determines the maximum time for data transfer. Once the time limit is reached, the process is canceled and the workflow continues with a corresponding message. | 5000 |
Workflow Setup
Upload Files to AWS
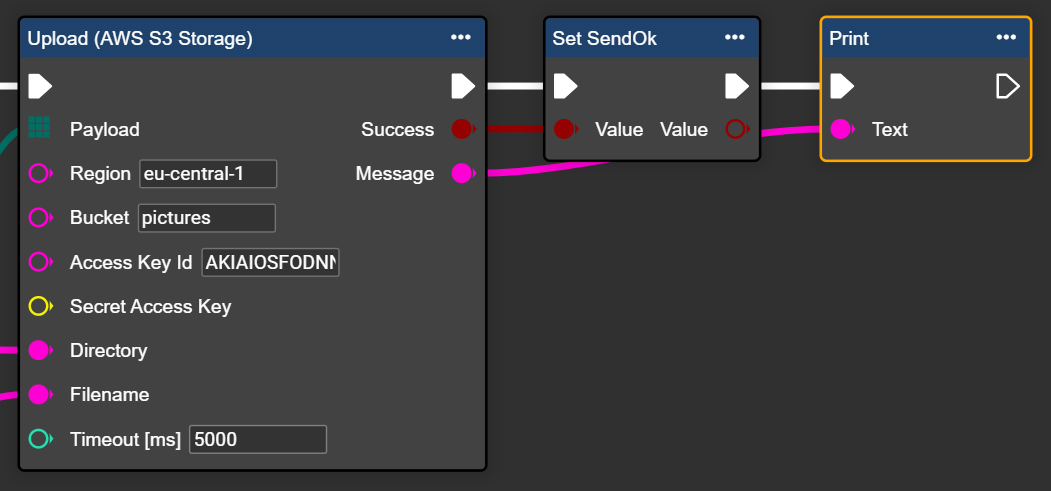
Open the context menu with a right-click and search for the node “Upload (AWS S3 Storage)”.
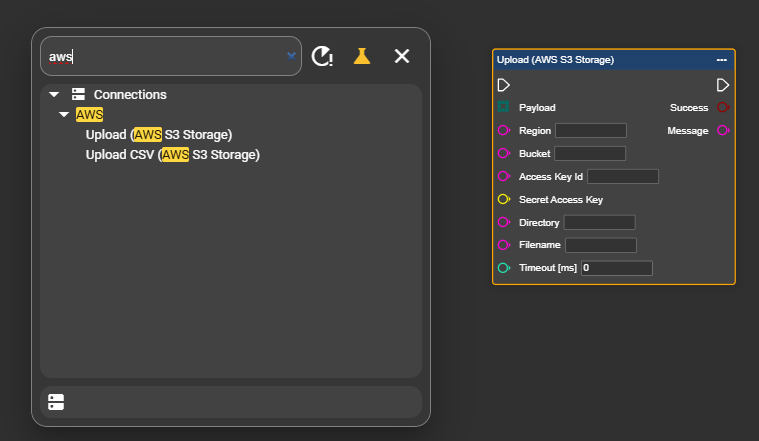
Now enter your connection parameters for the upload:
Region: eu-central-1 for Frankfurt, look List AWS
Access Key Id:
AKIAIOSFODNN7EXAMPLESecret Access Key
Bucket: pictures
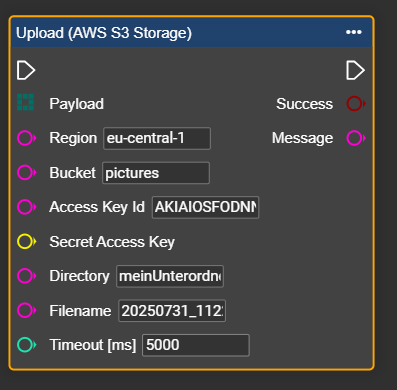
Connect the other parameters dynamically or store fixed values.
In the example shown, the file name and folder name are generated dynamically. The folder is created anew for each day and filled with the images taken on that particular day. The images are given file names based on a combination of the date and time stamp.
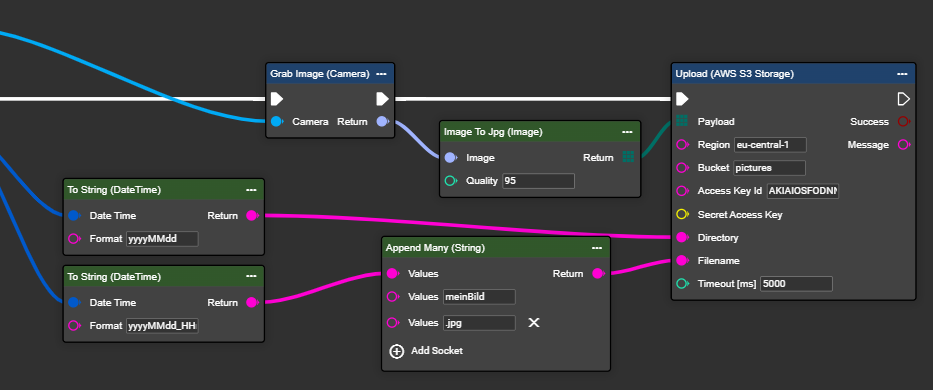
Congratulations! You can now successfully upload data to the cloud.
If problems arise: Please check whether your IT department has approved the firewall for the system.
The “Success” and “Message” outputs provide feedback on the transmission status and any error messages.
Fun Fact
By the way, you can quickly copy images from Azure to AWS using the following flow. To set up the Azure Storage Blob Camera, follow the instructions at Azure .