Kafka
The evoVIU camera supports a native Kafka producer connection, enabling the direct transfer of image data, metadata, or test results to an Apache Kafka cluster. This allows for seamless integration into modern, scalable data architectures and streaming pipelines.
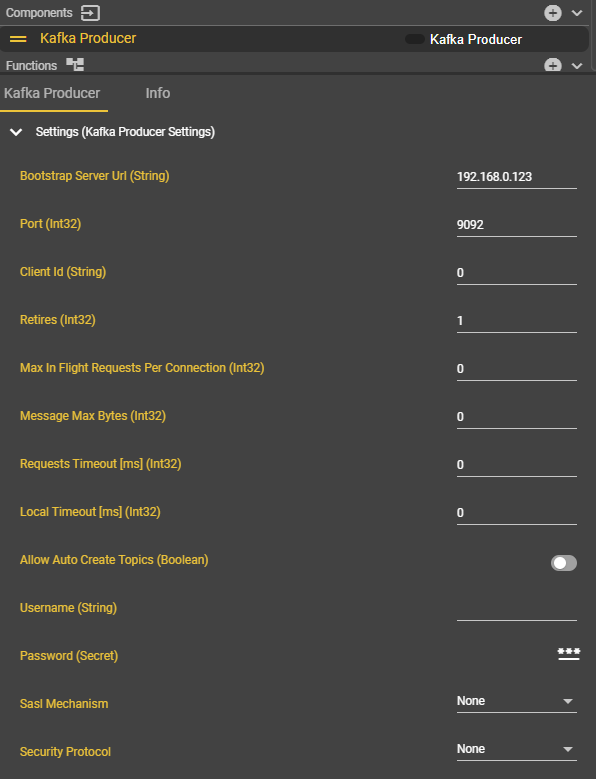
Kafka brokers (e.g., kafka01:9092) and the desired topic can be configured via the web interface. For structured processing, data can be sent in JSON, binary, or Avro format. The choice of format depends on the specific use case: JSON for easy readability, binary/Avro for efficient processing of large image data.
Sending can be cyclical, event-driven (e.g., for OK/NOK results), or triggered manually. Each message is timestamped; if necessary, a key for partitioning can also be defined.
The Kafka connection is particularly robust: reliable, secure communication can be ensured by configuring acknowledgments, retries, and optional SASL/SSL encryption.
With this integration, evoVIU can be flexibly integrated into distributed systems, cloud infrastructures, or analysis platforms (e.g., Kafka Streams, Spark) – ideal for Industry 4.0 or IIoT scenarios.
Connection parameters
Parameter | Type | Unit | Explanation | Example | Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Bootstrap Server Uri | Domain || IP - String | The destination address of the Kafka server. | mykafka.myfacory.de |
| |
Port | Integer | The port of the Kafka connection. | 9092 |
| |
ClientID | String | The client ID is a unique name used to identify a Kafka client at the broker. | 0 | ||
Retries | Integer | Number of transmission attempts in case of transmission error. | 1 |
| |
Max In Flight Request per Connection | Integer | Specifies how many requests can be sent in parallel without a response. | 0 | ||
Message Max Bytes | Integer | Byte | Sets the maximum size of a message. Value 0 = any size message | 0 | |
Requests Timeout | Integer | ms | Specifies the maximum time the client waits for a response. Value 0 = any length of waiting time | 0 | |
Local Timeout | Integer | ms | Sets the maximum timeout for producing, including retries. Value 0 = any length of waiting time | 0 | |
Allow Auto Create Topics | Bool | Allows topics to be created automatically upon access. | False | ||
Username | String | The username for authentication. | Not used | ||
Passwort | String | The password for authentication. | Not used | ||
SASL Mechanism | Dropdown | Specifies the auth method. | None | ||
Security Protocol | Dropdown | Defines the connection protocol. | None |
Workflow Setup
Anlage der Komponente Kafka Producer
In Workflows, under Components, go to ➕.
Search for the “Kafka Producer” component and select it.

A new component named "Kafka-Producer" will appear. This can be renamed at any time.
Enter the connection parameters.
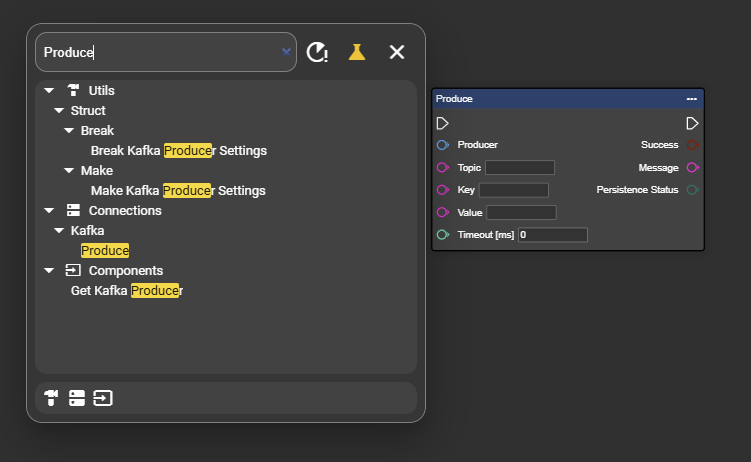
Right-click on your event graph to open the context menu.
Search for “Get Kafka Producer” and select the entry to add the node to the event graph.
Congratulations - The “Kafka Producer” component has been successfully created.
Sende Data via Kafka Producer
First, it is important to explain the individual inputs in this component independently of the connection data:
Input | Explanation | Example |
|---|---|---|
Topic | A topic is a logical channel through which messages are published and read. |
|
Key | The key determines the partition of a message. Identical keys always end up in the same partition. |
|
Value | The value is the actual message data content that producers send and consumers read. |
|
In the context menu, search for “Producer” and select “Get Kafka Producer”.
Connect the output of the “Get Kafka Producer” component to the “Producer” input of the Produce node.
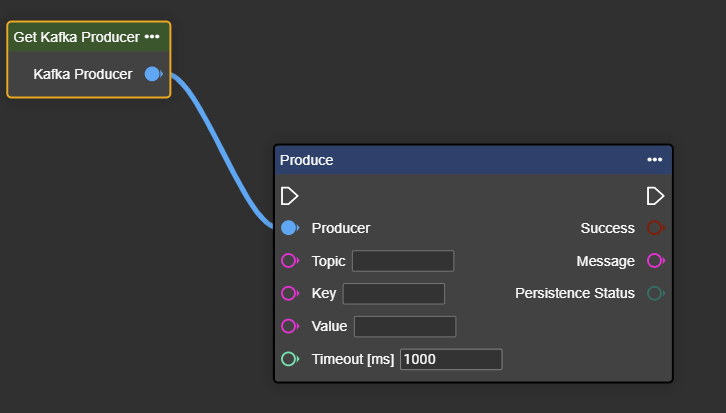
Enter the respective topic and key values provided to you. At the same time, you can link the corresponding data under Value.
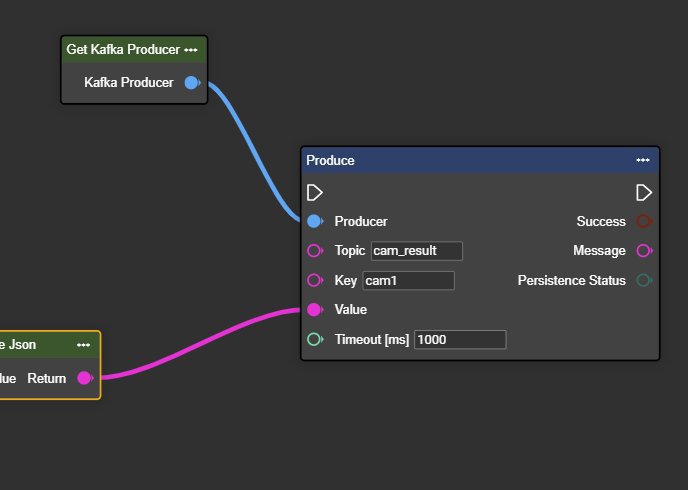
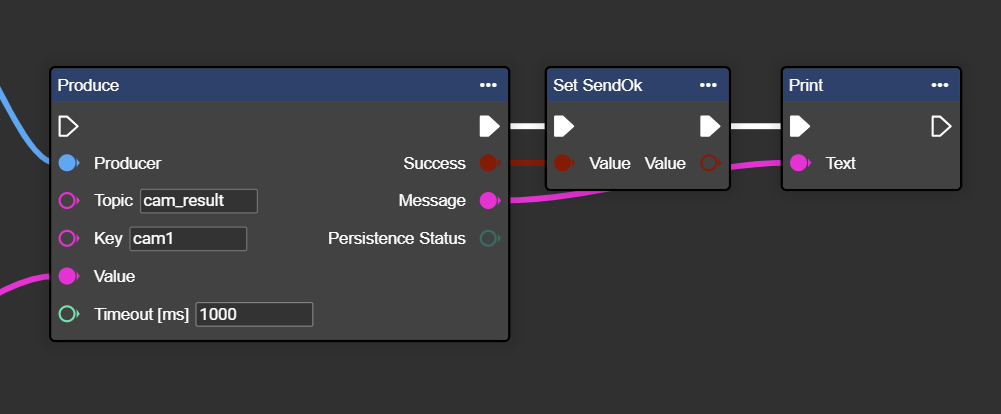
Congratulations! You can now successfully send data to the Kafka consumer.
If you want to see whether the data was transferred successfully, you can further process and output the “Success” and “Message” outputs at the end of the “Produce” node.