Morphology
Erode
Erode gradually removes the edges of a white foreground object in an image by converting non-white pixels to black. This reduces the size of the white areas, which is useful for eliminating small white spots or separating connected objects in the image.
Flow
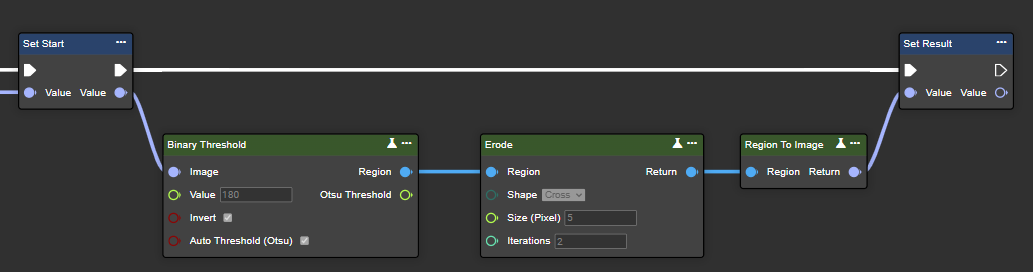
Parameter set
Attribute | Type | Description | First iteration | Last iteration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Region | Region | Binary image processed in black and white after segmentation. |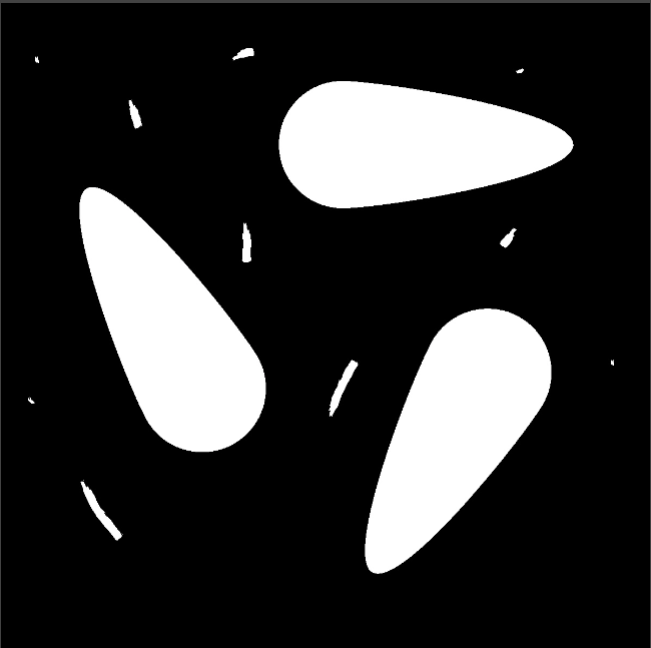  |  |
Shape | MorphShape |
| ||
Size (Pixel) | Single | This refers to the dimensions of the kernel used in the operation. A larger kernel size increases the area around each pixel, which affects how much the image is morphologically altered. | ||
Iteration | Int32 | Indicates how often the morphological operation is applied. The more iterations are performed in the erosion process, the smaller the white areas become. | ||
Return | Region | Binary image after morphological transformation. |
Dilate
Dilation gradually expands the boundaries of white foreground objects in an image by coloring pixels white if at least one pixel below the kernel is white. This increases the size of the white areas, effectively filling gaps and/or connecting separated parts of objects in the image.
Flow
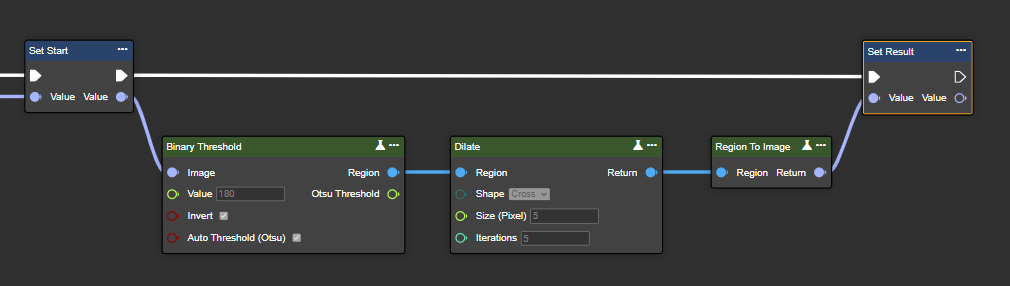
Parameter set
Attribute | Type | Description | First iteration | Last iteration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Region | Region | Binary image processed in black and white after segmentation. |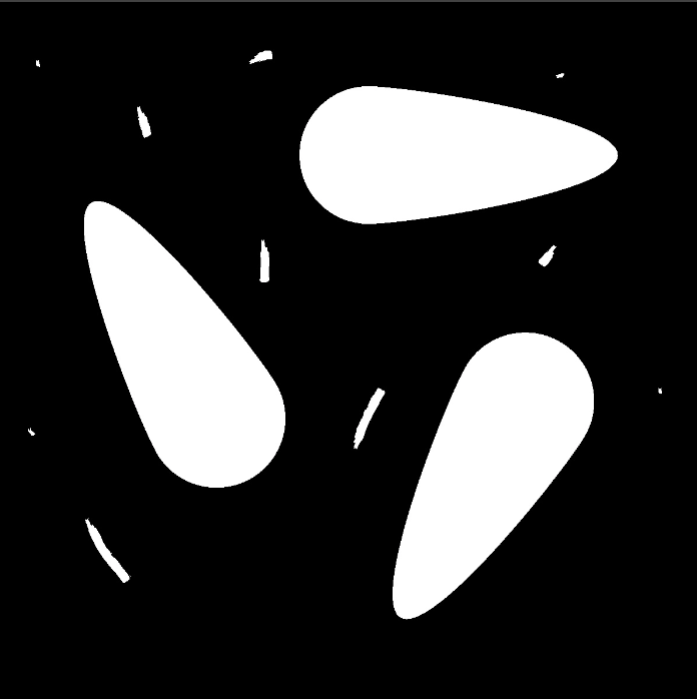  |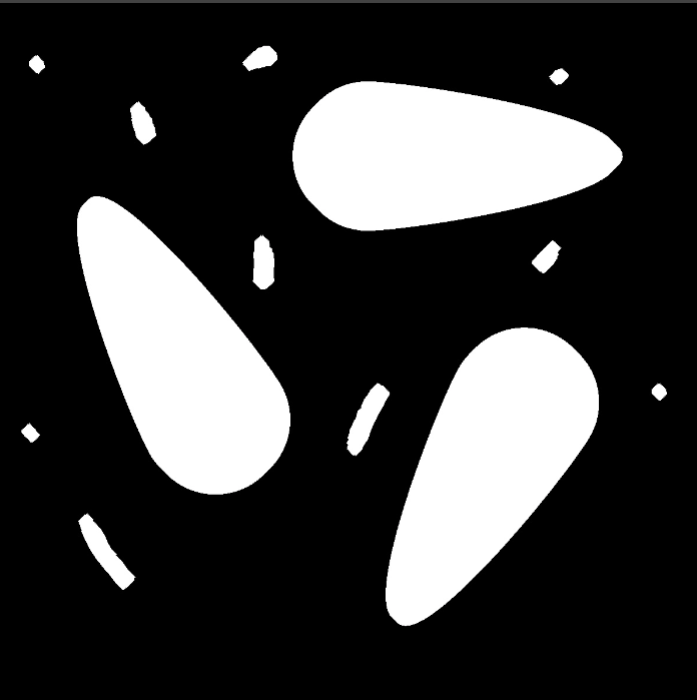  |
Shape | MorphShape |
| ||
Size (Pixel) | Single | This refers to the dimensions of the kernel used in the operation. A larger kernel size increases the area around each pixel, which affects how much the image is morphologically altered. | ||
Iteration | Int32 | Indicates how often the morphological operation is applied. The more iterations are performed in the dilation process, the larger the white areas become. | ||
Return | Region | Binary image after morphological transformation. |
Open
The Open function first applies erosion and then dilation to an image. This smooths edges, removes small protrusions, and separates overlapping objects by first shrinking and then enlarging the white areas in the image. This process is particularly effective for cleaning up noisy images or preparing them for further analysis, such as object recognition.
Flow
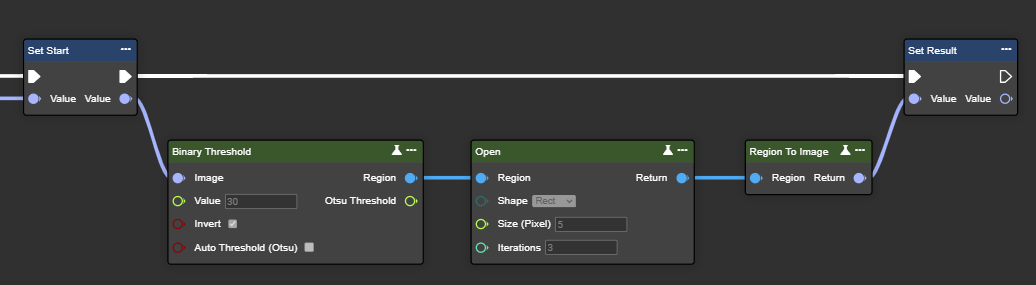
Parameter set
Attribute | Type | Description | First iteration | Second iteration | Last iteration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Region | Region | Binary image processed in black and white after segmentation. |  |  |  |
Shape | MorphShape |
| |||
Size (Pixel) | Single | This refers to the dimensions of the kernel used in the operation. A larger kernel size increases the area around each pixel, which affects how much the image is morphologically altered. | |||
Iteration | Int32 | Indicates how many times the morphological operation is applied. The more iterations are performed, the stronger the smoothing effect on the boundaries of the white foreground objects. | |||
Return | Region | Binary image after morphological transformation. |
Close
The "Close" function first applies dilation and then erosion to an image. This closes small gaps between white areas, connects broken parts of objects, and smooths irregularities in the foreground. This process is useful for filling small holes or cracks in objects and ensuring continuity in segmented areas of the image.
Flow
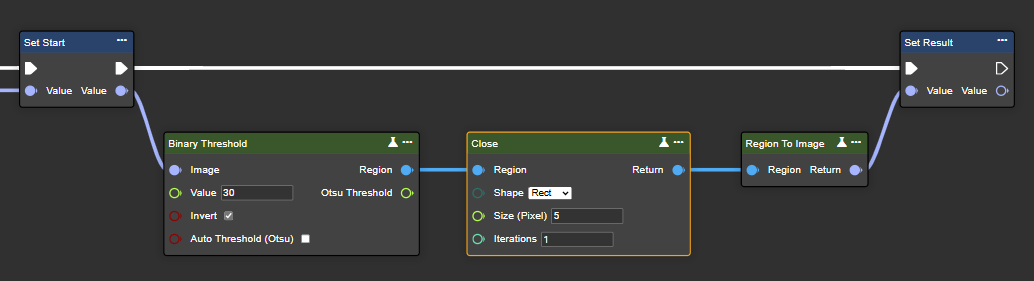
Parameter set
Attribute | Type | Description | First iteration | Second iteration | Last iteration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Region | Region | Binary image processed in black and white after segmentation. |  |  |  |
Shape | MorphShape |
| |||
Size (Pixel) | Single | This refers to the dimensions of the kernel used in the operation. A larger kernel size increases the area around each pixel, which affects how much the image is morphologically altered. | |||
Iteration | Int32 | Indicates how often the morphological operation is applied. More iterations effectively fill more gaps and smooth out irregularities in the foreground. | |||
Return | Region | Binary image after morphological transformation. |
Gradient
Gradient calculates the difference between dilation and erosion in an image, thereby highlighting edges and object outlines. It is particularly useful for tasks such as edge detection.
Flow
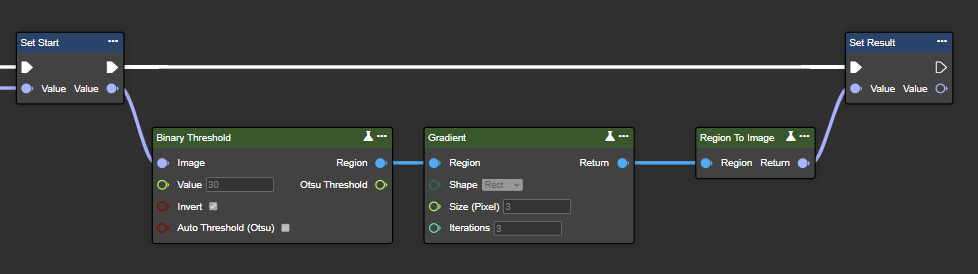
Parameter set
Attribute | Type | Description | First iteration | Second iteration | Last iteration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Region | Region | Binary image processed in black and white after segmentation. |  |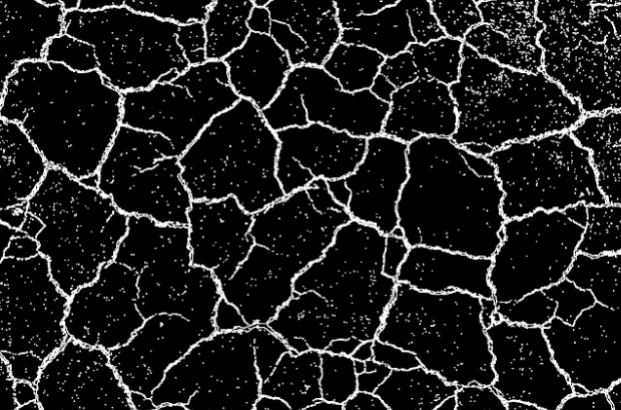  |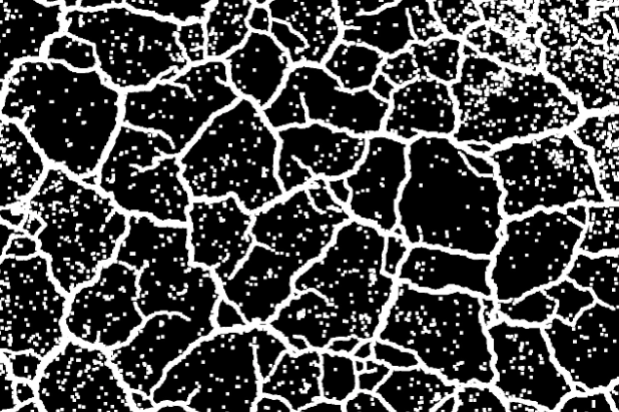  |
Shape | MorphShape |
| |||
Size (Pixel) | Single | This refers to the dimensions of the kernel used in the operation. A larger kernel size increases the area around each pixel, which affects how much the image is morphologically altered. | |||
Iteration | Int32 | Indicates how many times the morphological operation is applied. The more iterations are performed, the more pronounced the edges and boundaries become in the image. | |||
Return | Region | Binary image after morphological transformation. |
Top Hat
Top-hat processing calculates the difference between the original image and its opening. This operation is effective for highlighting small, bright details or features in the image, such as fine textures or noise.
Flow
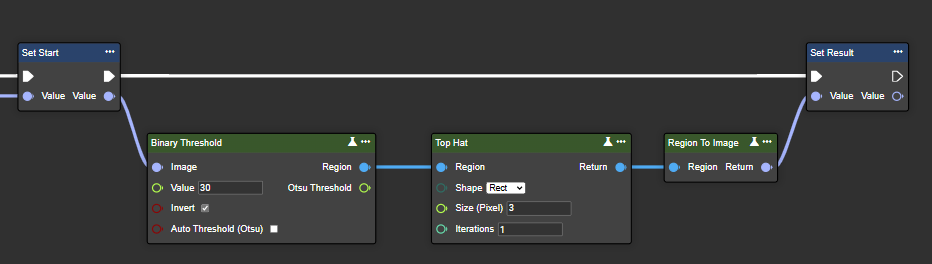
Parameter set
Attribute | Type | Description | First iteration | Second iteration | Last iteration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Region | Region | Binary image processed in black and white after segmentation. |  | 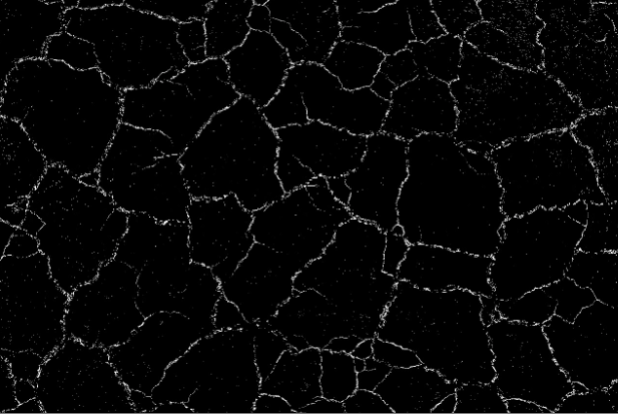 | 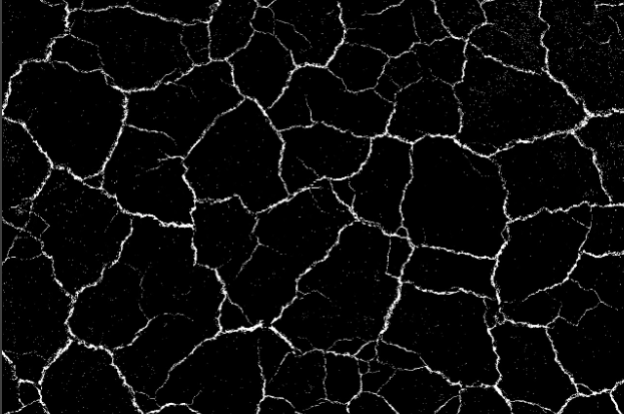 |
Shape | MorphShape |
| |||
Size (Pixel) | Single | This refers to the dimensions of the kernel used in the operation. A larger kernel size increases the area around each pixel, which affects how much the image is morphologically altered. | |||
Iteration | Int32 | Indicates how many times the morphological operation is applied. The more iterations are performed, the more the small, bright details in the image are highlighted and emphasized. | |||
Return | Region | Binary image after morphological transformation. |
Black Hat
Black-hat processing calculates the difference between the closing of an image and the original image. This operation is useful for identifying and highlighting small, dark features or details in the image, such as spots or dark objects on a lighter background.
Flow
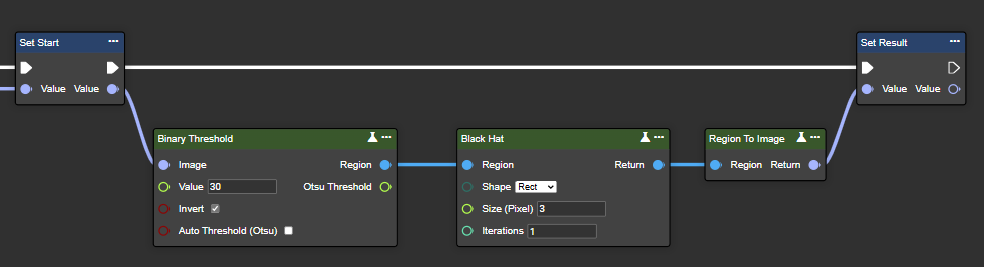
Parameter set
Attribute | Type | Description | Original | Closing | Abgleich |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Region | Region | Binary image processed in black and white after segmentation. |  |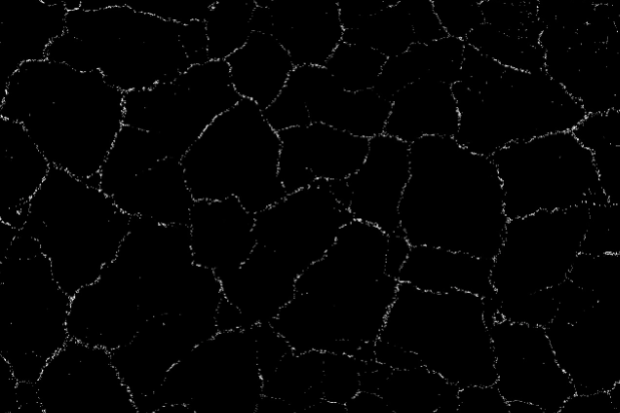  |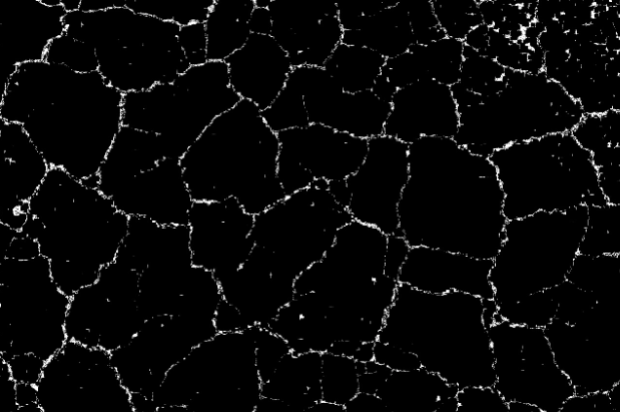  |
Shape | MorphShape |
| |||
Size (Pixel) | Single | This refers to the dimensions of the kernel used in the operation. A larger kernel size increases the area around each pixel, which affects how much the image is morphologically altered. | |||
Iteration | Int32 | Indicates how many times the morphological operation is applied. The more iterations are performed, the more strongly small, dark features and details in the image are emphasized. | |||
Return | Region | Binary image after morphological transformation. |
Hit Miss
Hit-miss detection recognizes specific patterns in an image by comparing foreground and background conditions defined by two complementary structural elements (kernels). It identifies precise pixel configurations and is useful for accurate shape or pattern recognition tasks in image processing.
Flow
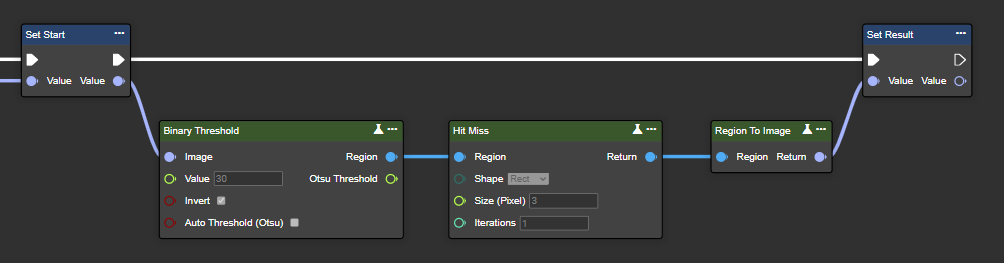
Parameter set
Attribute | Type | Description | Original | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Region | Region | Binary image processed in black and white after segmentation. | 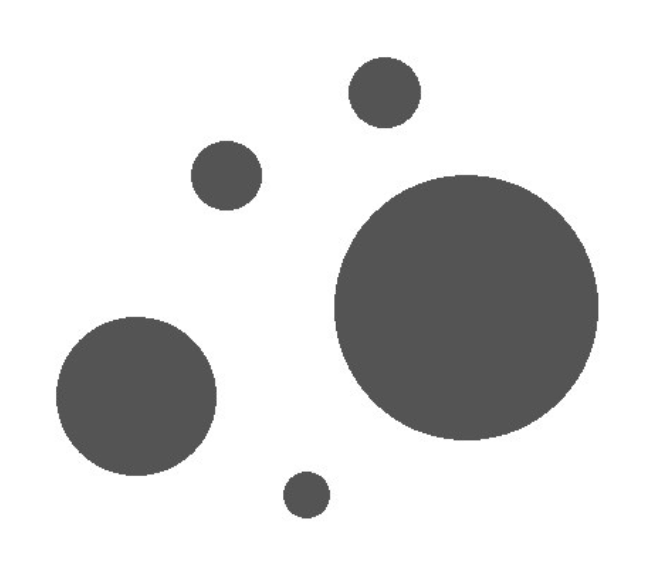 | 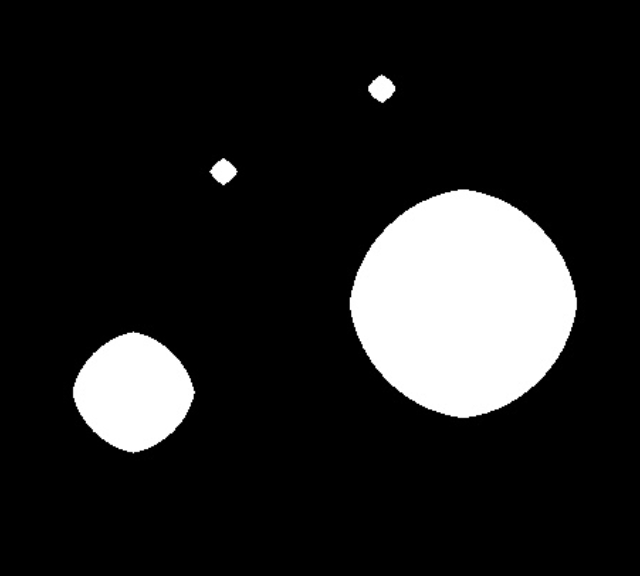 |
Shape | MorphShape |
| ||
Size (Pixel) | Single | This refers to the dimensions of the kernel used in the operation. A larger kernel size increases the area around each pixel, which affects how much the image is morphologically altered. | ||
Iteration | Int32 | Indicates how often the morphological operation is applied. The more iterations are performed, the more accurately certain patterns and shapes in the image are recognized based on the defined structural elements. | ||
Return | Region | Binary image after morphological transformation. |
