Segmentation
Adaptive Threshold
Adaptive thresholding adjusts the threshold for each pixel based on its local environment, thus handling varying lighting conditions within the image. This method improves accuracy, particularly in situations where the lighting in the image is uneven. It is used to reveal fine details or structures that would be lost with a global (uniform) threshold.
Flow
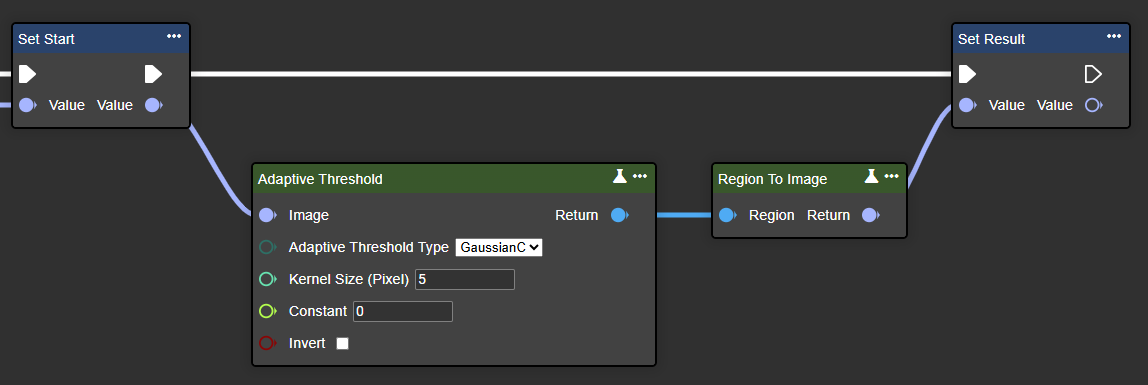
Parameter set
Attribute | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
Image | Image | A grayscale or color image is possible. |  |
Adaptive Threshold Type | AdaptiveThresholdType |
As a result, GaussianC usually reacts somewhat more robustly to noise and slight brightness fluctuations in the image than MeanC.. | In the example: GaussianC |
Kernel Size (Pixel) | Int32 | This parameter sets the size of the neighborhood area (a square window). A larger block size generally results in smoother, more consistent results because more pixels are considered when calculating the local threshold. A smaller block size, on the other hand, produces sharper and more detailed edges, but can also be more susceptible to noise. | In the example: 5 |
Constant | Single | This is a constant value that is subtracted from the calculated mean or Gaussian-weighted sum to determine the final threshold. Using such a constant helps reduce noise and fine-tune the threshold to local brightness conditions. | In the example: 0 |
Invert | Boolean | If this parameter is set to "true", the pixel values are inverted: Black pixels become white and white pixels become black. | In the example: false |
Return | Region | A binary image where each pixel is either black or white, thus representing areas that are above or below the calculated threshold. |  |
Binary Threshold
Pixel values below the threshold are set to 0 (black), and those above the threshold to 255 (white). This is suitable when there are clear contrast ratios or when the brightness differences in the image are strong enough, e.g., with a bright object on a dark background.
Important: If the Auto Threshold is set, the values in Value will be overwritten.
Flow
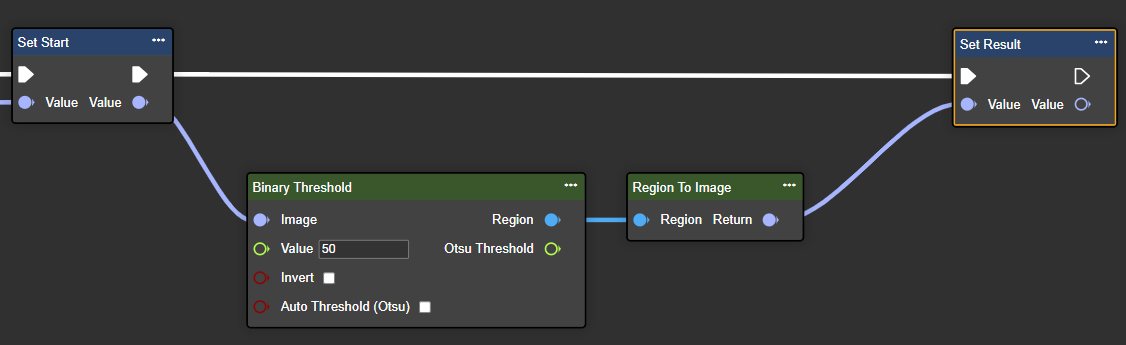
Parameter set
Attribute | Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
Image | Image | A grayscale or color image is possible. |  |
Value | Single | Threshold: Pixels whose brightness is above this value are set to 255 (white), while pixels below it are usually set to 0 (black). | In the example: 50 |
Invert | Boolean | If this parameter is set to true, the pixel values are reversed: black pixels become white, and white pixels become black. | In the example: false |
Auto Threshold (Otsu) | Boolean | Otsu's automatic thresholding is a method that automatically determines an optimal threshold for image binarization by minimizing the intra-class variance between foreground and background pixels. It thus seeks the value at which the separation of light and dark areas in the image is clearest. | In the example: false |
Region | Region | A binary image where each pixel is either black or white. | |
Otsu Threshold | Single | If Auto Threshold is enabled, this value contains the automatically calculated threshold (Otsu method); otherwise, the manually entered value is used. |  |
Color Threshold
Use this node to selectively isolate objects or areas of a specific color in an image. The color can be defined as an RGB color using Make Color or an existing color in the image can be detected using Detect Color.

The RGB value of the ROI can be determined using the Color Picker.
Each pixel is checked to see if its color lies within a defined color range.
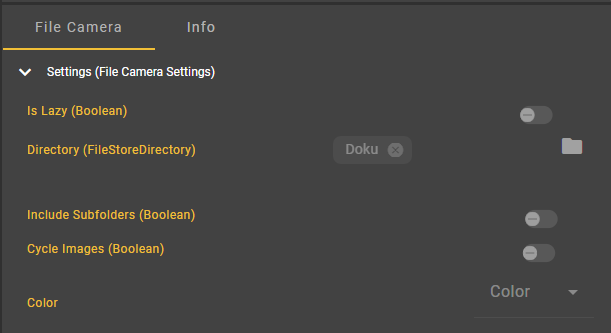
Important: Switch to color image in the File Camera Settings.
Flow
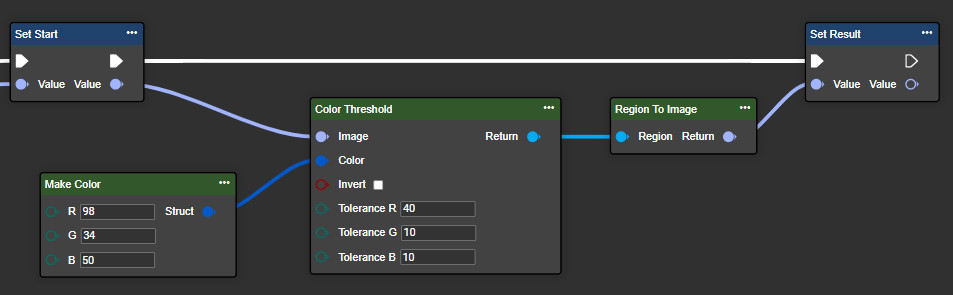
Parameter set
Attribute | Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
Image | Image | Color image. | 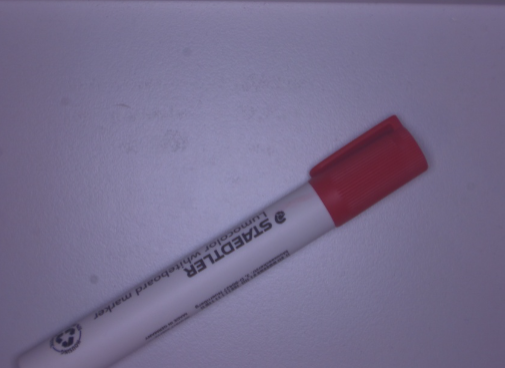 |
Color | Color | Reference color (RGB) | (255,0,0) |
Invert | Boolean | If this parameter is set to true, the mask is inverted so that all pixels outside the defined color range are selected. | |
Toleranz R | Byte | Tolerance around the red color (value range: 0–255), which indicates how much the color may deviate from the target value so that a pixel is still recognized as red. | In the example: 40 |
Toleranz G | Byte | Tolerance around the green color (value range: 0–255) | In the example: 20 |
Toleranz B | Byte | Tolerance around the blue color (value range: 0–255) | In the example: 20 |
Region | Region | A binary image where each pixel is either black or white. | 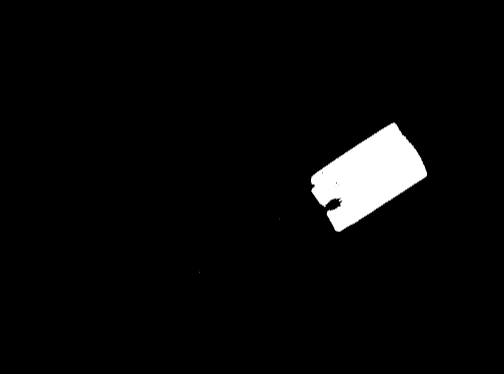 |
To Zero Threshold
Pixel values below the threshold are set to zero, while values above the threshold remain unchanged. This method preserves more detail of the original image for pixels above the threshold.
Flow
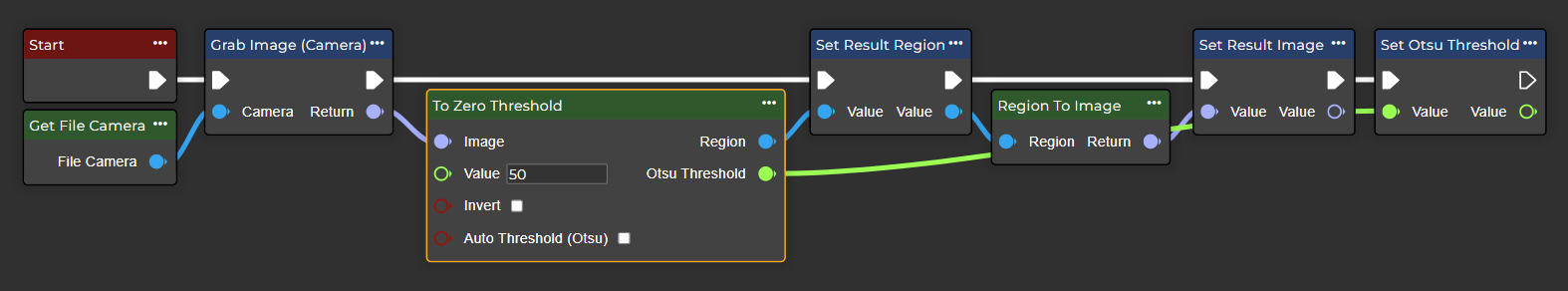
Parameter set
Attribute | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
Image | Image | A grayscale or color image is possible. |  |
Value | Single | Threshold. Pixels whose intensity exceeds this value remain unchanged. | In the example: 50 |
Invert | Boolean | If set to true pixels above the chosen value will be set to black and those below will remain unchanged. | In the example: false |
Auto Threshold (Otsu) | Boolean | Otsu's automatic threshold determination is a method that automatically determines an optimal threshold for image binarization by minimizing the variance within the classes between foreground and background pixel intensities. | In the example: false |
Region | Region | A binary image in which the pixels are either black or white. |  |
Otsu Threshold | Single | If automatic threshold calculation is enabled, this field contains the automatically calculated threshold (Otsu method); otherwise, it contains the input value. |
