Filter
Arithmetic
Arithmetic algorithms modify images through mathematical operations on pixel values. They are not used to smooth, but rather to adjust contrast, brightness, or sharpness:
Deviation highlights deviations and makes differences in the image visible.
Emphasis enhances specific image areas or features.
Sharpening emphasizes edges and details for a sharper appearance.
Gamma Correction adjusts brightness and contrast depending on the image display (e.g., monitor adjustment).
Subtract highlights differences between two images or versions.
Pow (power transformation) specifically changes the brightness distribution to emphasize dark or light areas.
Depending on the project, these methods are suitable for image enhancement, analysis and adjustment.
Deviation
Detects deviations from the target value in the image – highlights areas that deviate from the expected pattern.
Flow
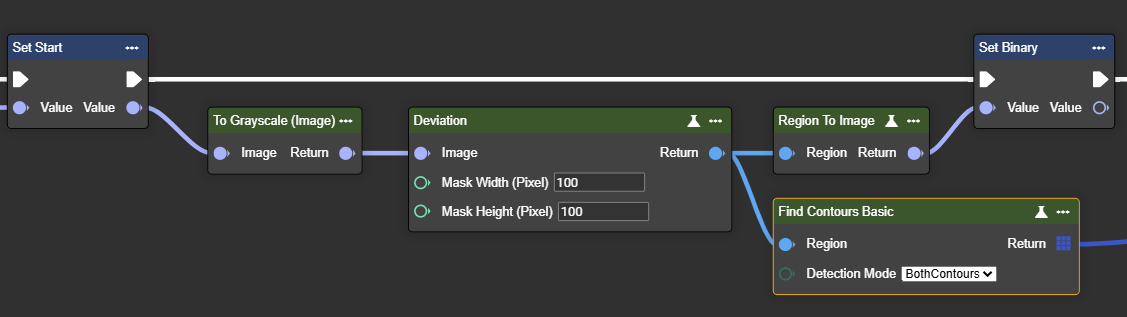
To achieve results, the color image must be converted to grayscale. This can be done using the "To Grayscale (Image)" node.
Parameter set
Parameter | Type | Description | Value range | Effect Min | Effect Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Image | Image | A grayscale image is required. You can use the "To Grayscale (Image)" node. |  |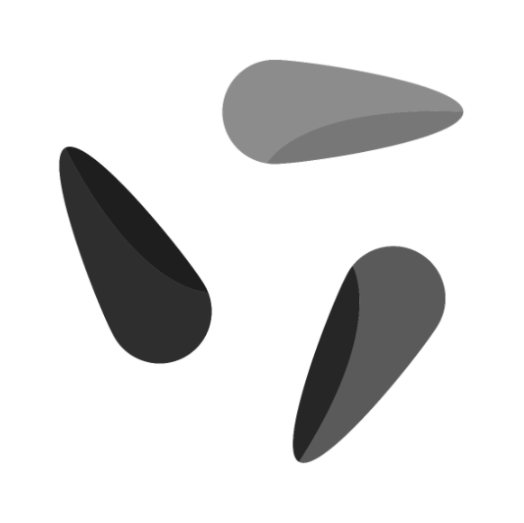  | |
Mask Width (Pixel) | Int32 | Set the width of the mask used for the deviation calculation. Larger values cover a wider area, helping to detect larger or more significant deviations. | Width: 5px 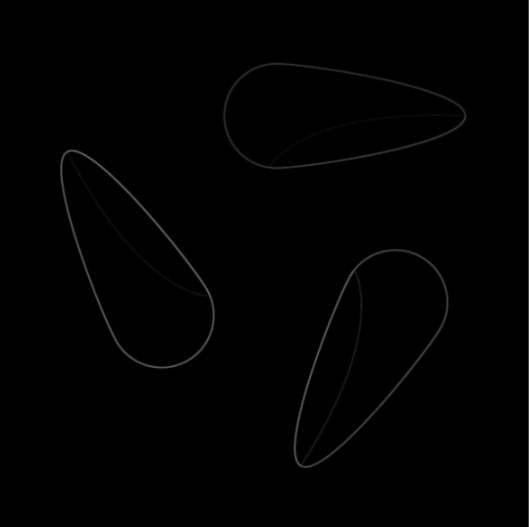 | Width: 200px 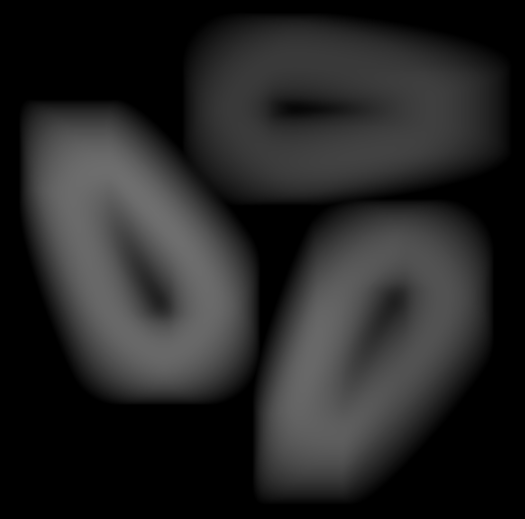 | |
Mask Height (Pixel) | Int32 | Set the height of the mask used for deviation calculation. Larger values cover a larger area, which helps detect larger or more significant deviations. | Width: 10px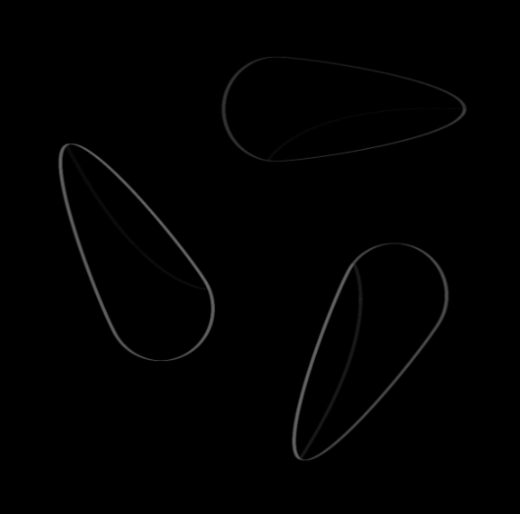  | Width: 2px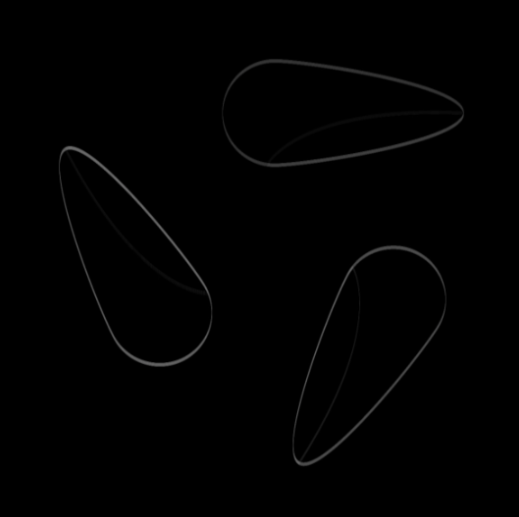  | |
Return | Region | A binary black-and-white image that highlights deviations from the expected pattern. This is useful for detecting anomalies or inconsistencies in the image. |
Emphaszie
Adjusts the contrast and brightness of an image – improves the appearance and visibility of details.
Flow
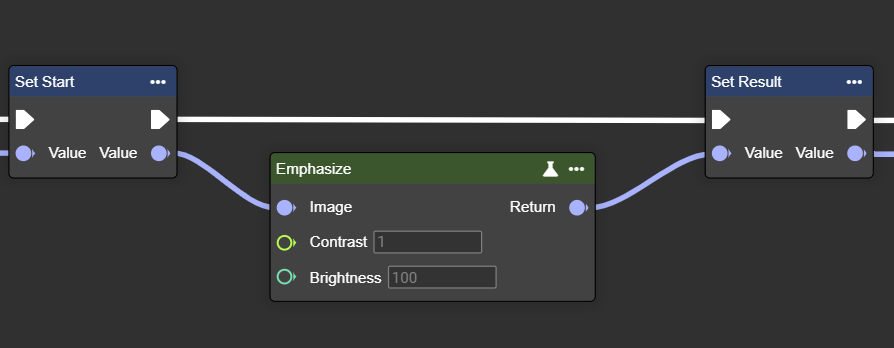
Parameter set
Parameter | Type | Description | Value range | Effect Min | Effect Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Image | Image → Input | Both grayscale and color images can be used. If a grayscale image is to be used, the image may need to be converted beforehand using the "To Grayscale (Image)" node. | |||
Contrast | Single | Adjustment factor to increase or decrease image contrast. A higher value emphasizes the differences between light and dark areas. | > 0.01 |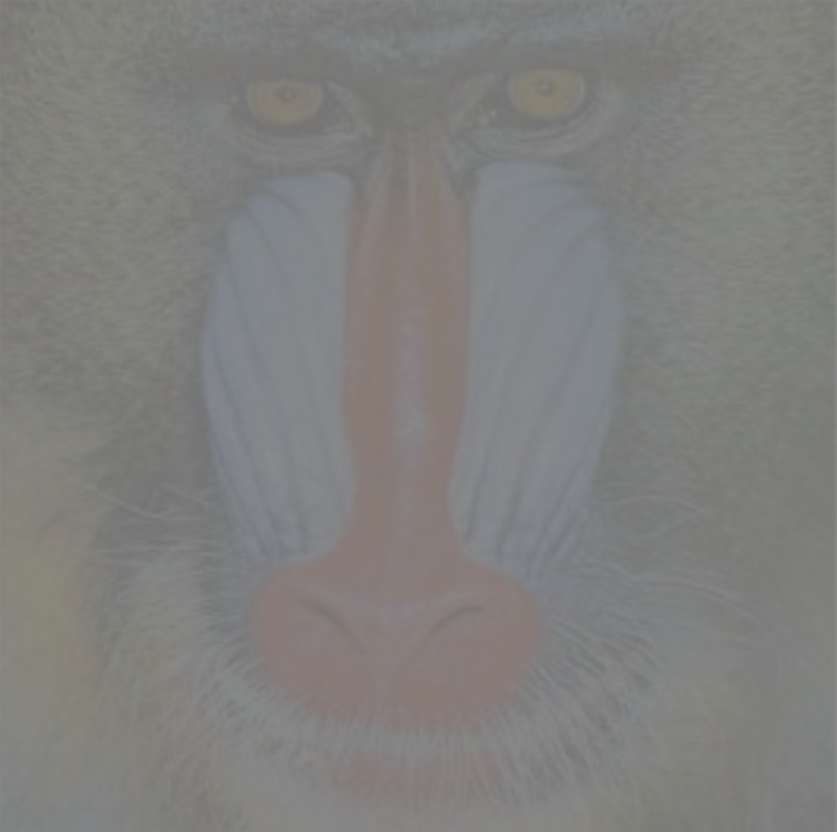  |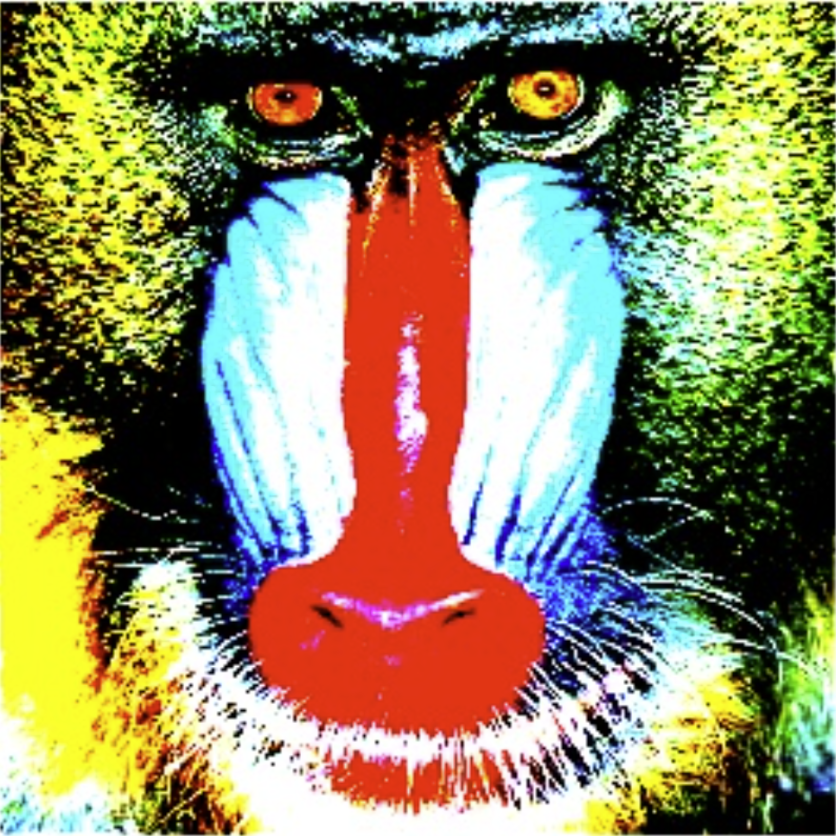  |
Brightness | Int32 | Higher values increase the overall brightness and make the image brighter. | >= 0 |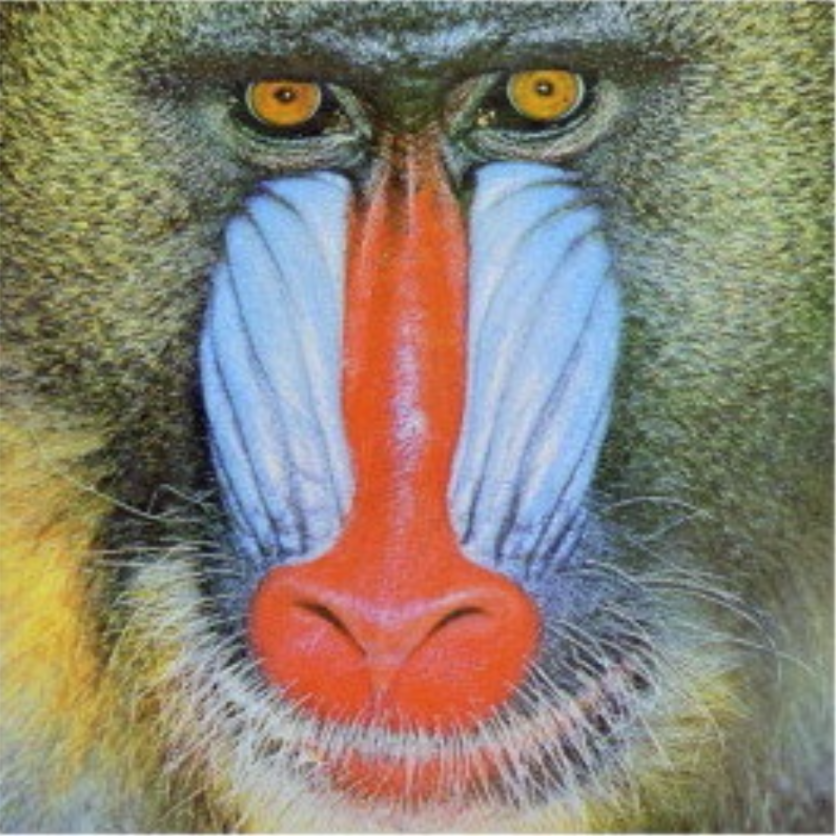  |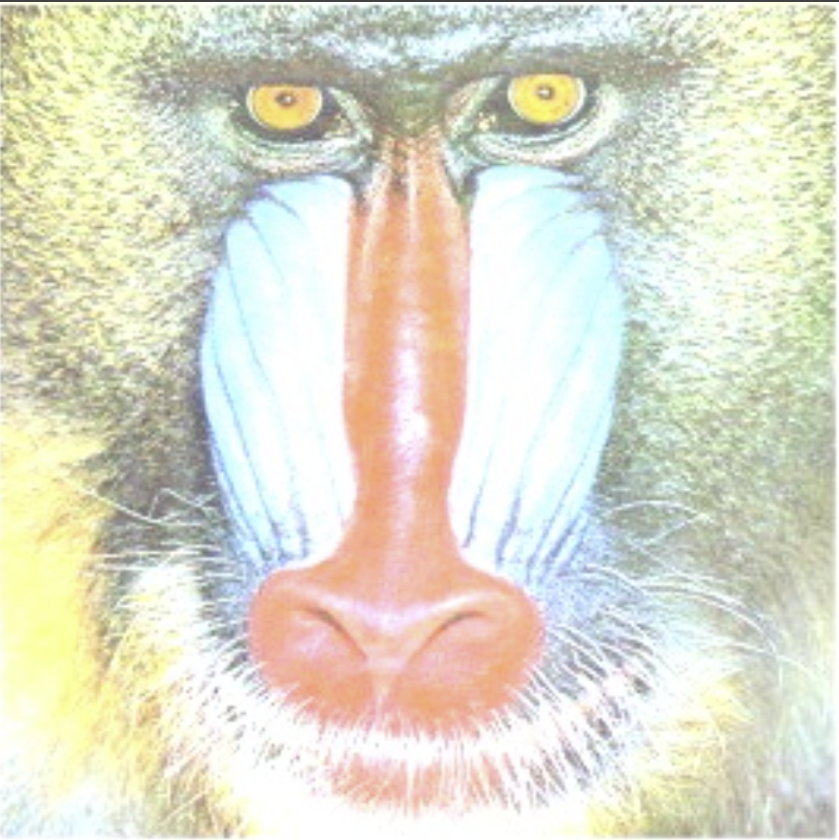  |
Sharpening
Sharpens an image by increasing the contrast between adjacent pixels – improving detail and clarity.
Flow
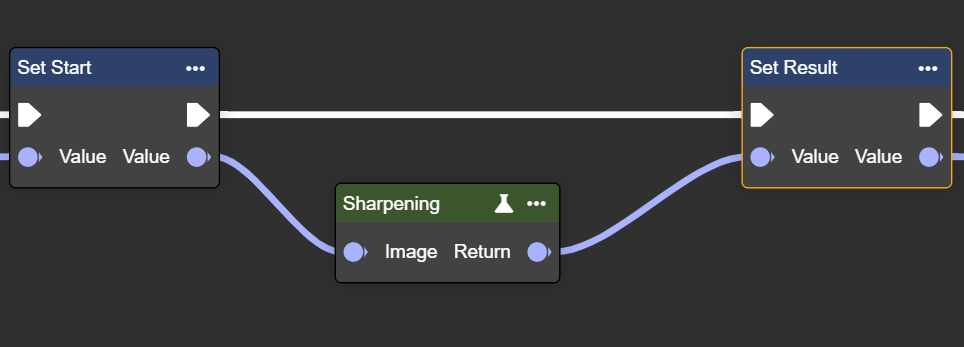
Parameter set
Parameter | Type | Description | Effect - Mono | Effect - Color |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Image | Image → Input | Both grayscale and color images can be used. If a grayscale image is to be used, the image may need to be converted beforehand using the "To Grayscale (Image)" node. |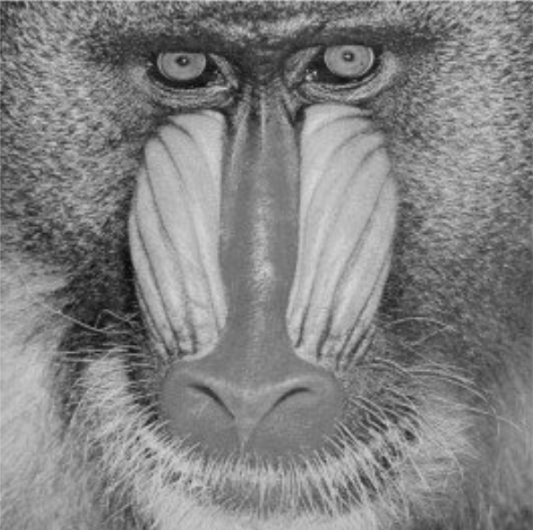  |  |
Image | Image → Output | Transformed image with improved sharpness. |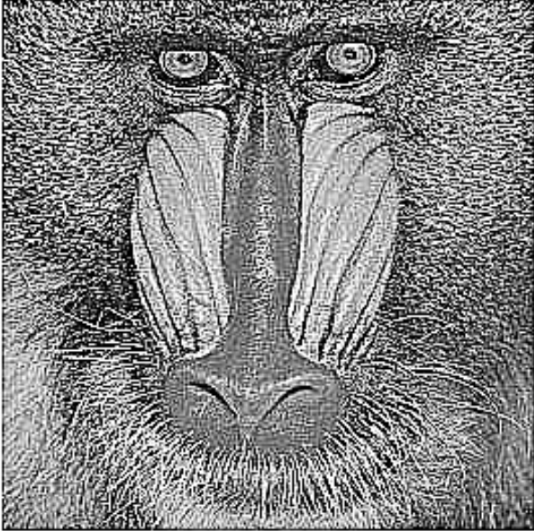  |  |
Gamma Correction
Adjusts the gamma value of the image – controls brightness and contrast for an optimized display.
Flow
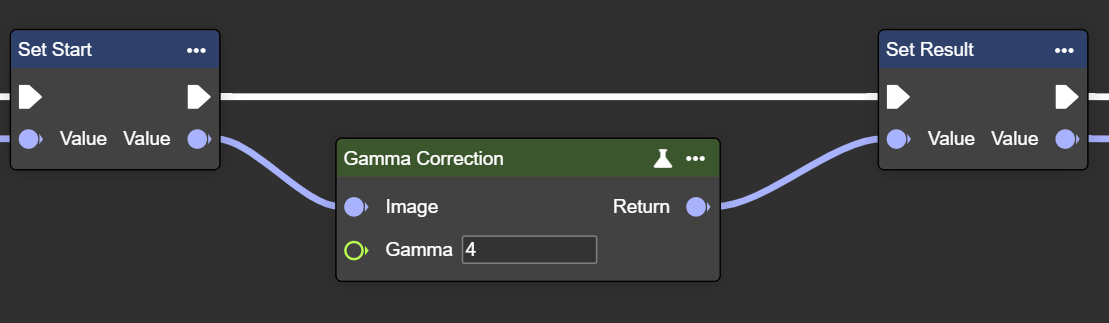
Parameter set
Parameter | Type | Description | Effect - Mono | Effect - Color |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Image | Image → Input | Both grayscale and color images can be used. If a grayscale image is to be used, the image may need to be converted beforehand using the "To Grayscale (Image)" node. |  |  |
Image | Image → Output | Higher values increase gamma correction, which emphasizes dark pixels and attenuates bright areas, allowing for better segmentation in darker areas of the image. |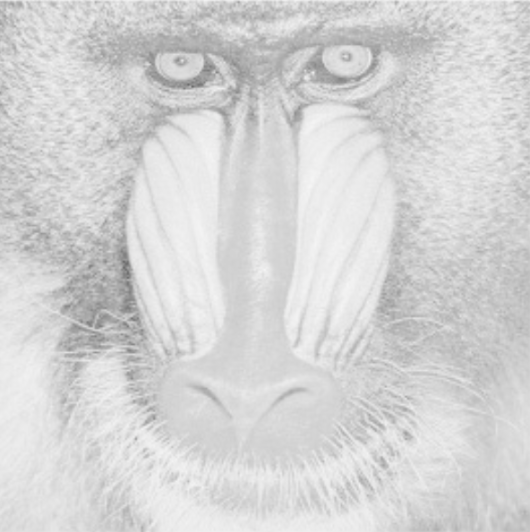  |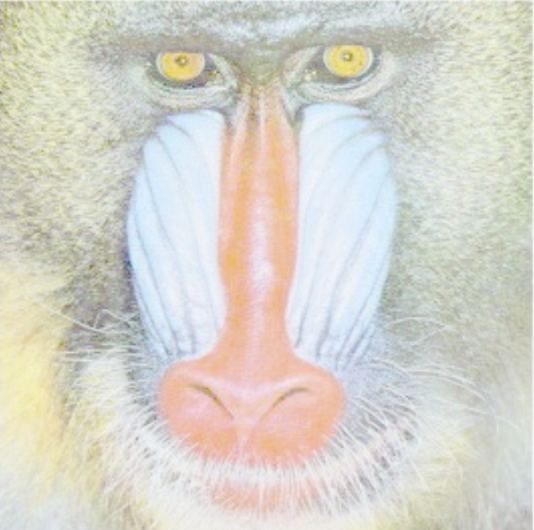  |
Substract
Subtracts pixel values from one image from another – highlights differences between the two images.
Flow
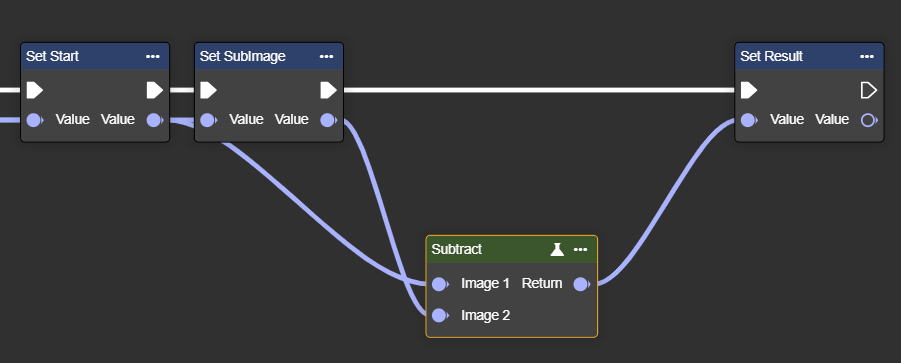
Parameter set
Parameter | Type | Description | Effect - Mono | Effect Color |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Image 1 | Image | The first image from which the pixel values are subtracted. |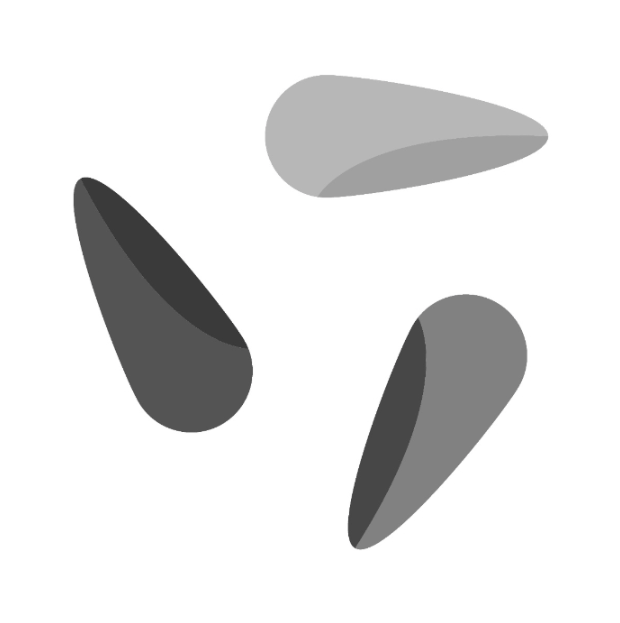  |  |
Image 2 | Image | The second image subtracted from the first image. |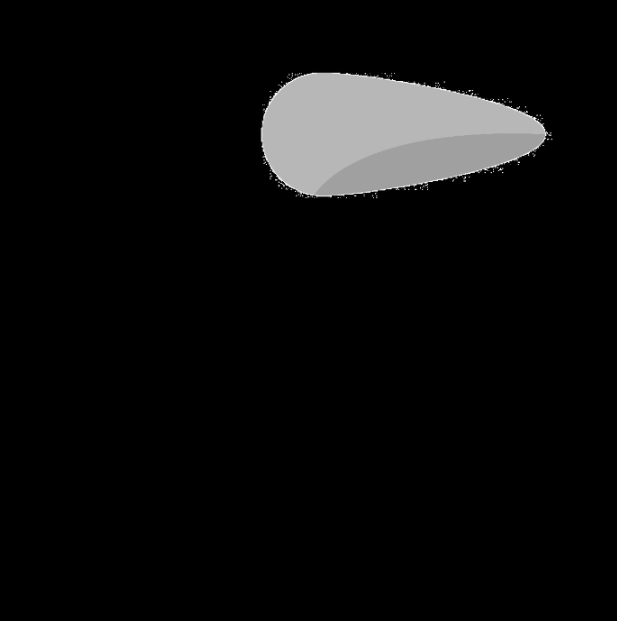  |  |
Return | Image | A new image showing the result of pixel-wise subtraction and highlighting the differences between the two input images. |  |  |
Pow
Raises pixel values to a power – increases or decreases brightness to enhance contrast or emphasize detail.
Flow
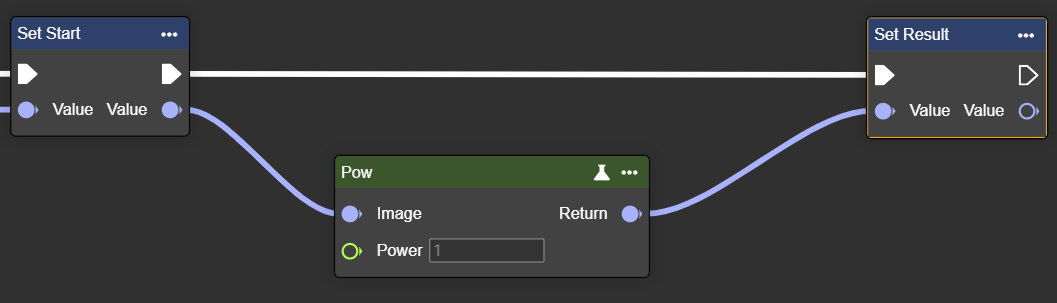
Parameter set
Parameter | Type | Description | Effect - Mono | Effect - Color |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Image | Image → Input | Both grayscale and color images can be used. If a grayscale image is to be used, the image may need to be converted beforehand using the "To Grayscale (Image)" node. |  |  |
Power | Single | The exponent by which each pixel value is increased - Example with Power = 1.1 |  |  |
Single |
Example with Power = 1.5 |  |  | |
Return | Image | See pictures of Power Example 1 and 2 |
Smoothing
Smoothing algorithms are used to reduce noise in images and make surfaces appear more uniform. Depending on the method, they vary in the degree to which details or edges are preserved:
The Average filter calculates the mean of the neighborhood and creates a simple blur.
The Bilateral filter combines spatial proximity and color similarity, smoothing surfaces while preserving edges.
The Gaussian filter gives more weight to nearby pixels, providing a smooth, even smoothing effect.
The Median filter replaces each pixel with the median of its surroundings and is particularly effective at removing point-like noise.
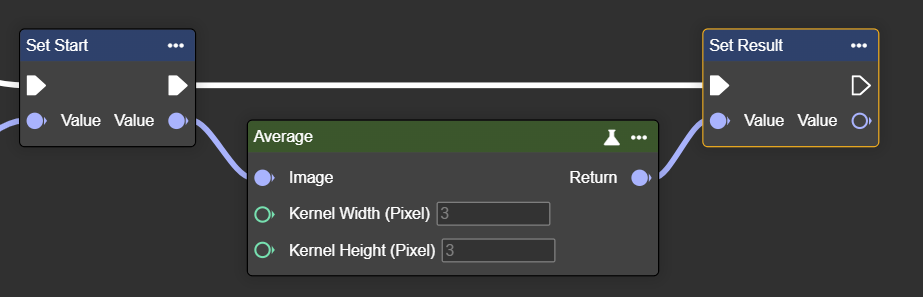
Average
Applies an averaging filter – smooths the image and reduces noise or grainy structures.
Please use only positive and odd parameters : 1,3,5,7 …
Flow
Parameter set
Parameter | Type | Description | Effect - Min | Effect - Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Image | Image → Input | Both grayscale and color images can be used. If a grayscale image is to be used, the image may need to be converted beforehand using the "To Grayscale (Image)" node. |  |  |
Kernel Width (Pixel) | Int32 | Width of the neighborhood used for averaging. Higher values increase smoothing but may blur details. The value must be positive and odd. |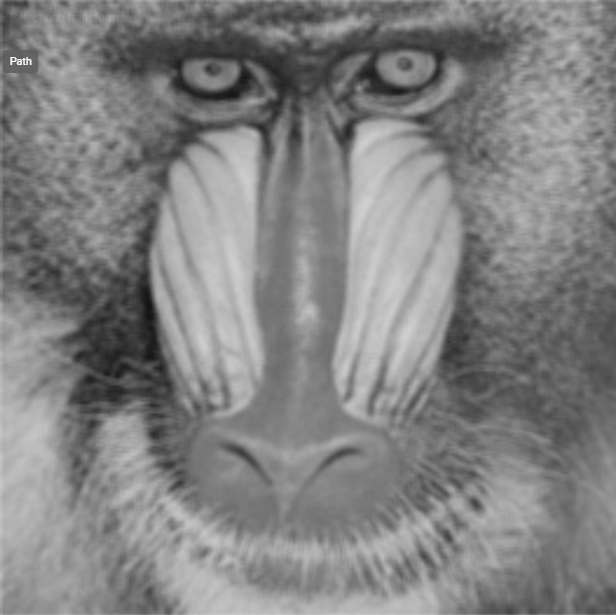  Width: 3px |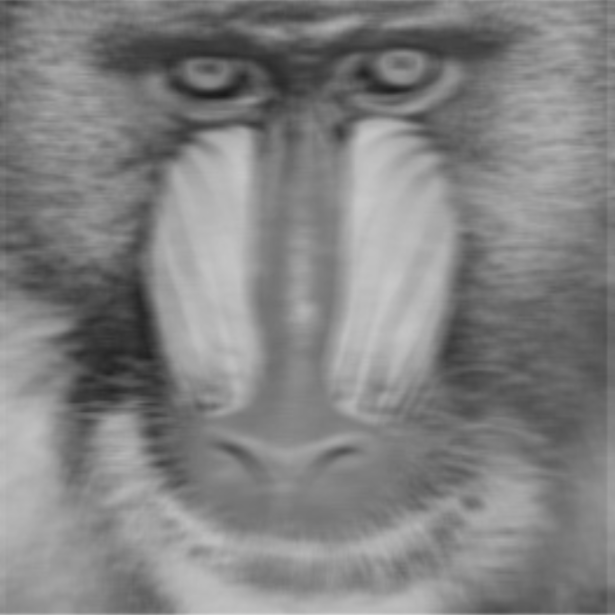  Width: 9px |
Kernel Height (Pixel) | Int32 | Height of the neighborhood used for averaging. Higher values increase smoothing but may blur details. The value must be positive and odd. |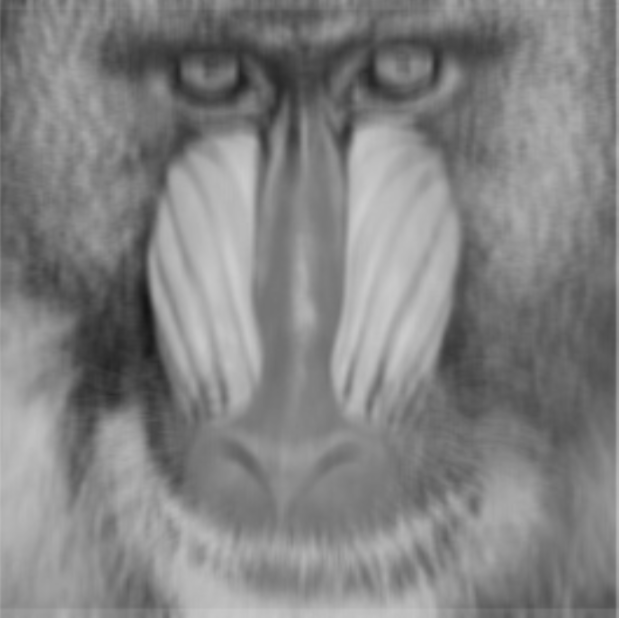  Width: 3px |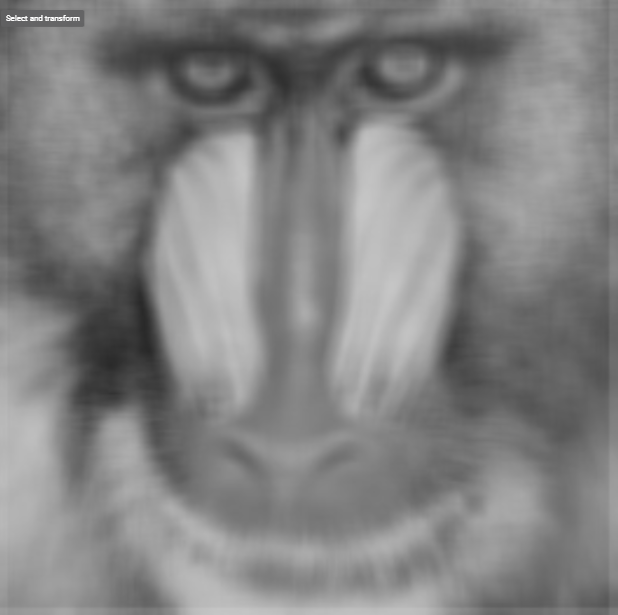  Width: 9px |
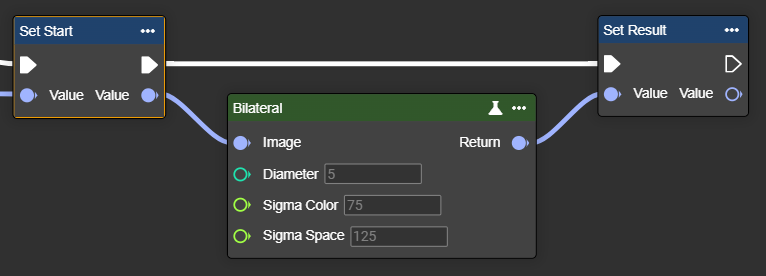
Bilateral
Bilateral smoothing is a noise reduction filter that smooths surfaces while preserving edges. Unlike simple blur filters, it takes into account both the distance between pixels and their color similarity.
Flow
Parameterset
Parameter | Type | Description | Value range | Effect Min | Effect Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Image | Image | Both grayscale and color images can be used. If a grayscale image is to be used, the image may need to be converted beforehand using the "To Grayscale (Image)" node. |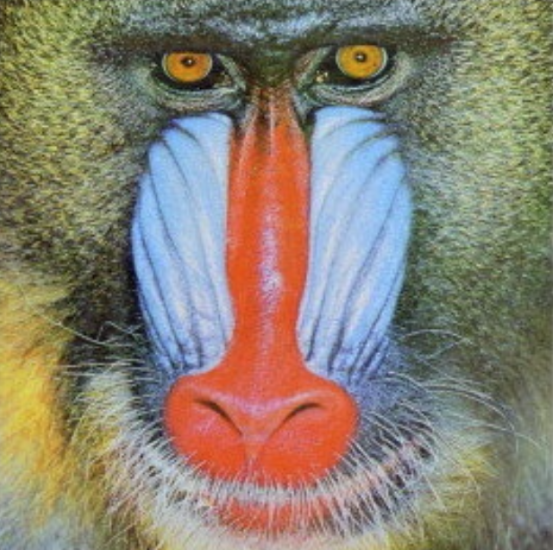  |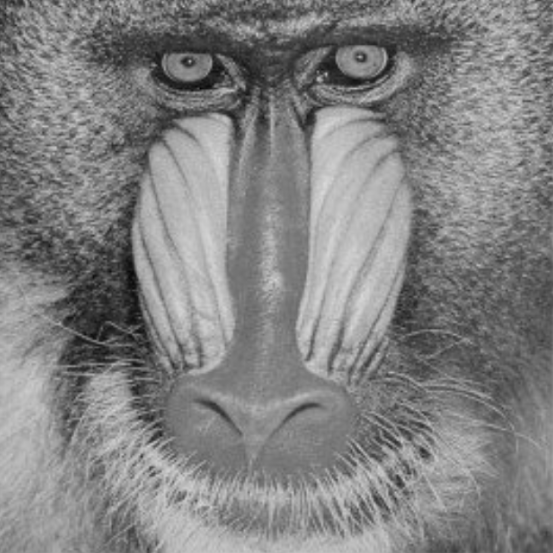  | |
Diameter | Int32 | Diameter of each pixel neighborhood used in filtering. Higher values increase smoothing. Diameter determines the size of the area considered:
| >0 |  Diameter:5 |  Diameter:25 |
Sigma Color | Single | Standard deviation of the color space, which affects how much the filter takes into account intensity differences between pixels. Higher values increase overall smoothness. SigmaColor controls the sensitivity to color differences:
| 0 - 254 |  Diameter:5 |  Diameter:5 |
Sigma Space | Single | Standard deviation of spatial distance, which affects how much the filter takes into account the proximity of pixels. At higher values, more distant pixels can influence the smoothing. SigmaSpace determines how much spatial distance counts:
| 0 - 254 |  Diameter:5 |  Diameter:5 |
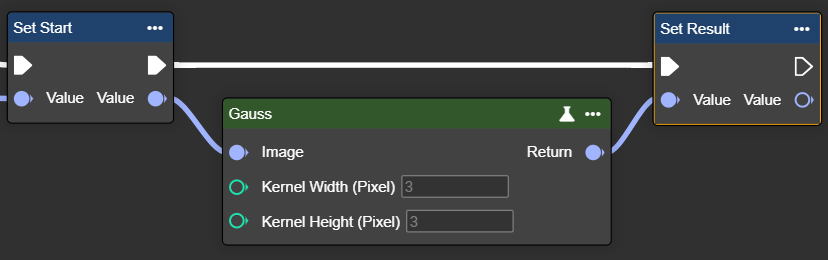
Gauss
Applies a Gaussian filter to an image and smooths it by averaging the pixel values within a specified Gaussian kernel size.
The Gaussian filter is suitable for smooth blurring and reducing fine noise. It is primarily used as a preprocessing step, for example, before edge detection.
Flow
Parameter set
Parameter | Type | Description | Effect - Min | Effect - Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Image | Image → Input | Both grayscale and color images can be used. If a grayscale image is to be used, the image may need to be converted beforehand using the "To Grayscale (Image)" node. |  | |
Kernel Width (Pixel) | Int32 | Width of the Gaussian kernel. Higher values increase smoothing but may blur details. The value must be positive and odd. |  Width: 3px |  Width: 9px |
Kernel Height (Pixel) | Int32 | Height of the Gaussian kernel. Higher values increase smoothing but may blur details. The value must be positive and odd. |  Width: 3px |  Width: 9px |
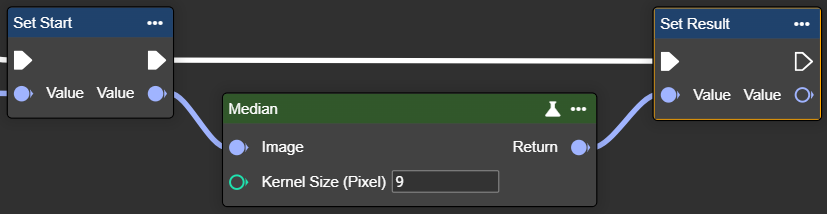
Median
This node allows you to apply a median filter to an image, which reduces noise by replacing each pixel value with the median value of its neighborhood.
The median filter is particularly useful for removing point-like "salt and pepper" noise. It smooths noise without blurring edges as much as average or Gaussian filters.
Flow
Parameter set
Parameter | Type | Description | Effect Min | Effect Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Image | Image | A grayscale image is required. You can use the "To Grayscale (Image)" node. |  | |
Kernel Size (Pixel) | Int32 | The range of neighboring pixels used to calculate the median. Higher values increase noise reduction but may blur fine details. The value must be positive, odd and greater than 1. |  Kernel Size: 3 |  Kernel Size: 11 |
Transformation
Transformation algorithms change the geometric representation of an image without directly editing its content. They are used to adjust size, orientation, or distortion:
Anisotropic Scaling changes the height and width independently (e.g., stretching or shrinking).
Isotropic Scaling enlarges or reduces the image evenly in all directions.
Resize adjusts the image to the desired size.
Translate moves the image by a specific amount in the x or y direction.
Flip mirrors the image horizontally or vertically.
Rotate Center rotates the image around its center point.
Undistort corrects distortions (e.g., caused by camera optics).
These methods are used to adjust, align or geometrically correct images.
Anisotropic Scaling
Scales the width and height of an image using different factors, enabling non-proportional resizing. In image processing, this is primarily used for correction and normalization, allowing objects to be analyzed consistently regardless of the recording conditions.
Flow
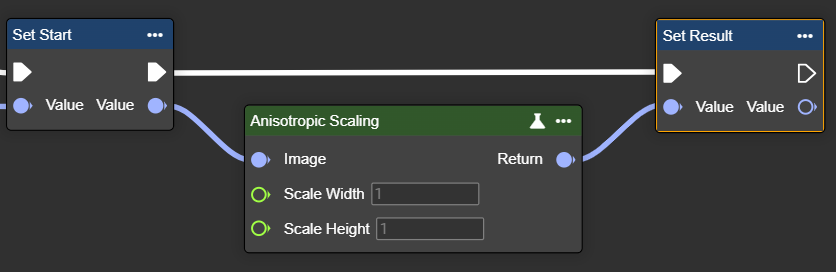
Parameter set
Parameter | Type | Description | Value range | Effect Min | Effect Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Image | Image | Both grayscale and color images can be used. If a grayscale image is to be used, the image may need to be converted beforehand using the "To Grayscale (Image)" node. |  Original = Scale 1 | ||
Scale Width | Single | Factor by which the image width is scaled. | Example values: |  Scale Width: 1 |  Scale Width: 2 |
Scale Height | Single | Factor by which the image height is scaled. | Example values: |  Scale Width: 0.1 |  Scale Width: 1.7 |
Isotropic Scaling
Scales an image evenly in both directions while maintaining the aspect ratio. Isotropic scaling ensures consistent scaling and is ideal when proportions and shapes need to be preserved exactly, for example, in AI or classification systems.
Flow
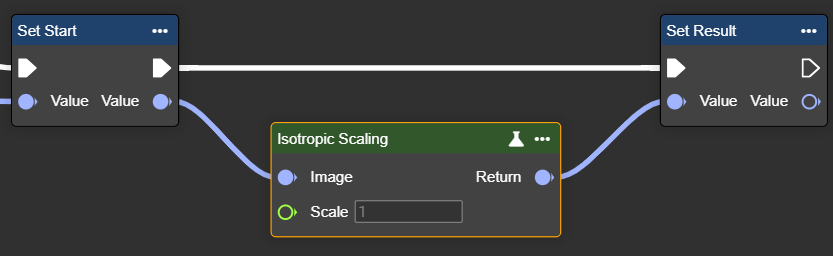
Parameter set
Parameter | Type | Description | Value range | Effect Min | Effect Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Image | Image | Both grayscale and color images can be used. If a grayscale image is to be used, the image may need to be converted beforehand using the "To Grayscale (Image)" node. |  Original = Scale 1 | ||
Scale | Single | Uniform scaling factor applied to both width and height. | Example values: |  Scale: 0.5 |  Scale: 3 |
Resize
Changes image size to defined dimensions – width and height are adjusted specifically to the desired number of pixels.
Flow
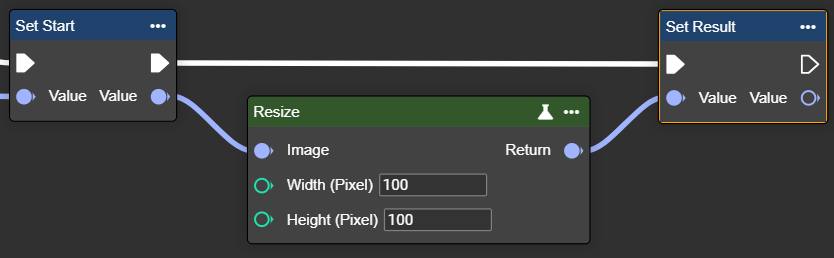
Parameter set
Parameter | Type | Description | Value range | Effect Min | Effect Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Image | Image | Both grayscale and color images can be used. If a grayscale image is to be used, the image may need to be converted beforehand using the "To Grayscale (Image)" node. |  | ||
Width | Int32 | Desired width in pixels. | >1 |  Width: 100px |  Width: 500px |
Height | Int32 | Desired height in pixels. | >1 |
Translation
Moves an image horizontally and/or vertically – free areas are filled with black pixels.
Flow
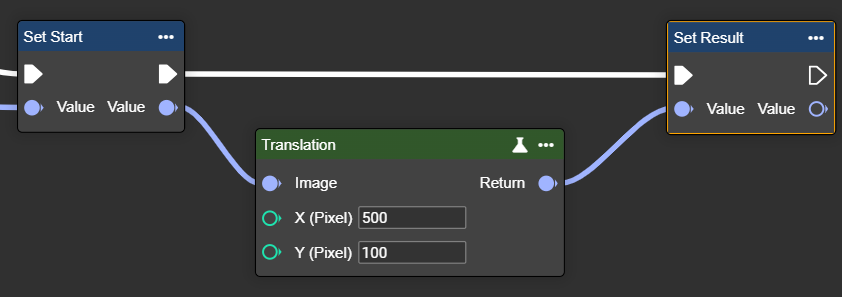
Parameter set
Parameter | Type | Description | Value range | Effect Min | Effect Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Image | Image | Both grayscale and color images can be used. If a grayscale image is to be used, the image may need to be converted beforehand using the "To Grayscale (Image)" node. |  | ||
X (Pixel) | Int32 | Horizontal offset. Positive values shift the image content to the right, while negative values shift it to the left. | >0 to the right |  X: 100px |  X: -250px |
Y (Pixel) | Int32 | Vertical offset distance. Positive values shift the image content downward, while negative values shift it upward. | >0 downward |  X: 150px |  X: -250px |
Flip
Flips an image horizontally or vertically – creates a mirror image along the selected axis.
Flow
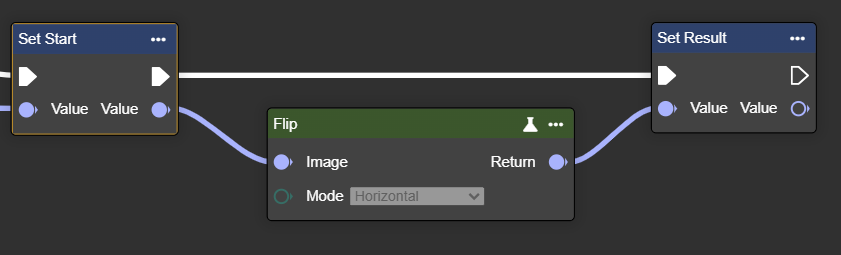
Parameter set
Parameter | Type | Description | Value range | Effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Image | Image | Both grayscale and color images can be used. If a grayscale image is to be used, the image may need to be converted beforehand using the "To Grayscale (Image)" node. |  | |
Mode | Enum 1 | Direction in which the image should be mirrored: | Horizontal |  |
Enum 2 | Direction in which the image should be mirrored: | HorizontalVertical |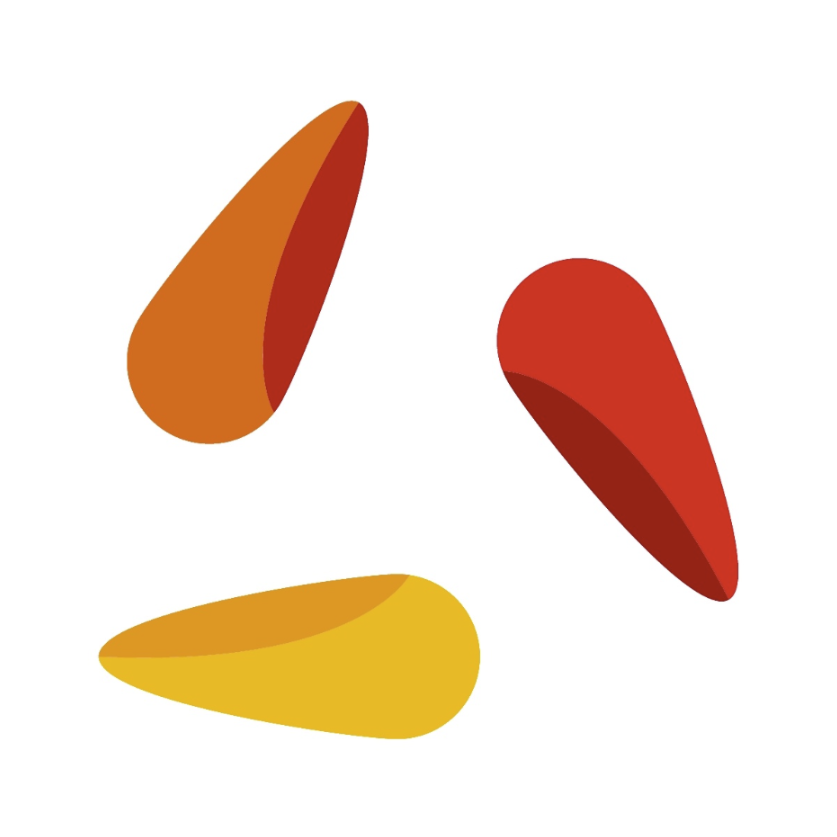  | |
Enum 3 | Direction in which the image should be mirrored: | Vertical |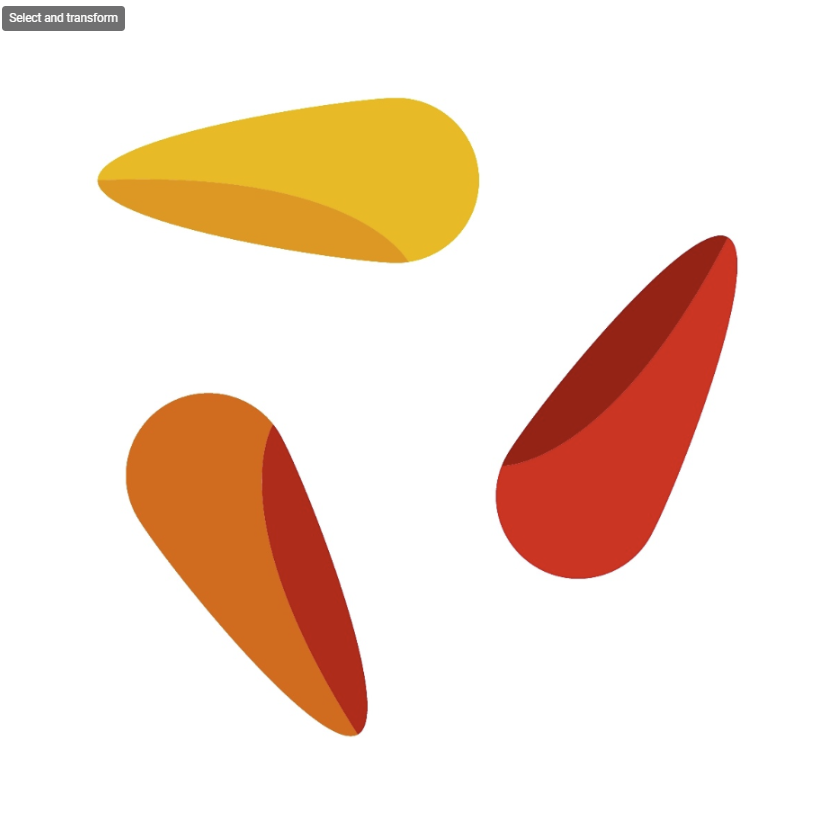  |
Rotate Center
Rotates an image by a specified angle – rotation occurs around the center.
Angle > 0: Rotation to the left
Angle < 0: Rotation to the right
Flow
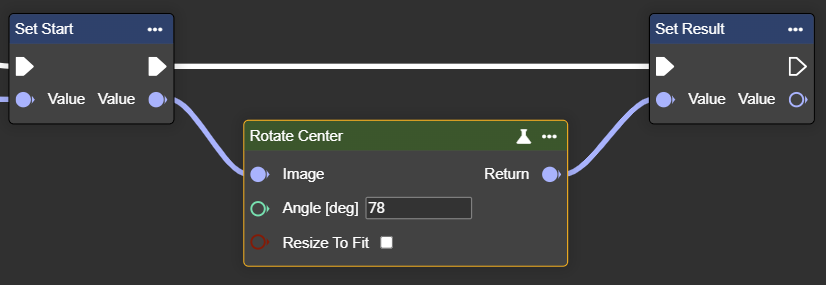
Parameter set
Parameter | Type | Description | Effect | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Image | Image | Both grayscale and color images can be used. If a grayscale image is to be used, the image may need to be converted beforehand using the "To Grayscale (Image)" node. |  | |
Angle [deg] | Int32 | Angle by which the image is rotated. Angle > 0: Rotation to the left Angle < 0: Rotation to the right |  Example: 15° |  Example: -45° |
Resize To Fit | Boolean |  Example: -45° |  Example: -45° |
Undistort
Removes the so-called fisheye effect from the image – corrects extreme wide-angle distortion.
We will provide the data upon request depending on the sensor and lens.
Flow
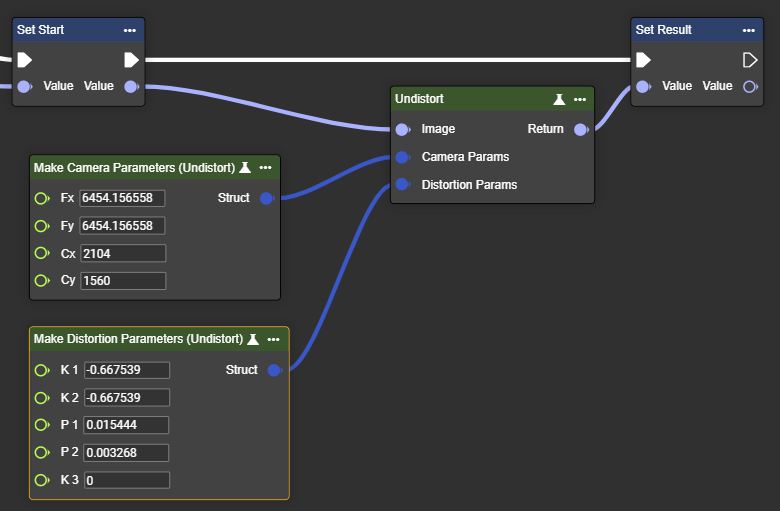
Parameter set
Parameter | Type | Description | Value range | Effect Min |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Image | Image | Both grayscale and color images can be used. If a grayscale image is to be used, the image may need to be converted beforehand using the "To Grayscale (Image)" node. |  | |
Camera Params | Camera Params |
Please use the “Make Camera Parameters (Undistort)” node for this. Fx: Focal length of the system (sensor - optics) in the x-direction We will provide the data upon request depending on the sensor and lens. | Example VIU13 - 2.6mm lens: |  |
Distortion Params | Distortion Params |
Please use the “Make Distortion Parameters (Undistort)” node for this. K1: Distortion parameter K1 We will provide the data upon request depending on the sensor and lens. | Example VIU13 - 2.6mm lens: |
